This is T-Minus, where we count down the biggest developments in space, from new rocket launches to discoveries that advance our understanding of the universe and our place in it. Humanity is reaching new heights in space exploration. Make sure you’re part of the journey by subscribing here.
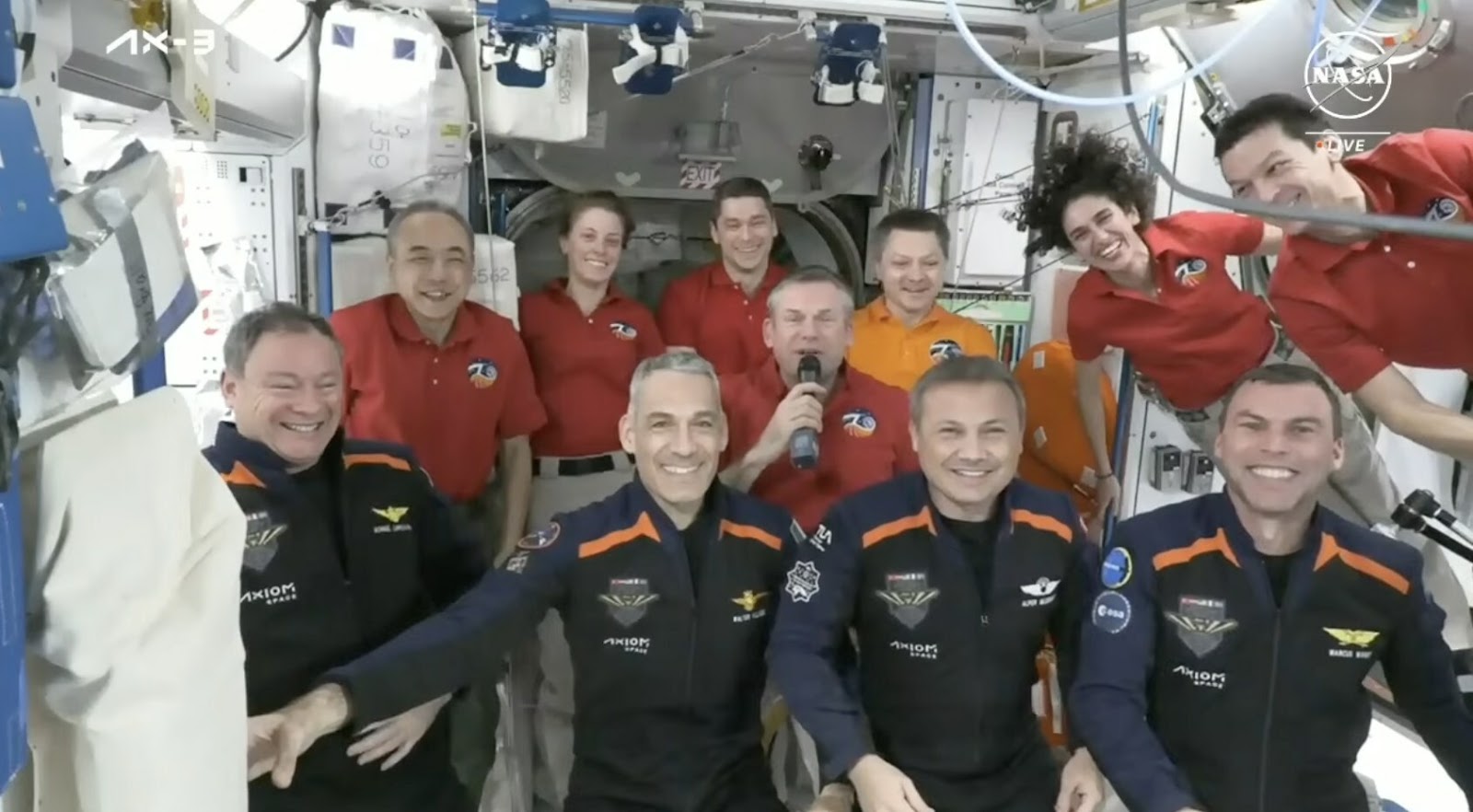


Private crew visits the ISS
On January 20, the International Space Station got a little more crowded — and a lot more diverse — when the four members of Texas-based startup Axiom Space’s AX-3 mission joined the seven astronauts already on board the orbiting science lab.
The private crew will now spend 14 days conducting experiments and demoing tech on the ISS before catching a ride back to Earth via a SpaceX Crew Dragon on February 3.
This was Axiom’s third all-private mission to the ISS and the first to feature an all-European crew, with one astronaut each from Spain, Italy, Sweden, and Turkey — the Turkish passenger, Alper Gezeravcı, is now the first person from his nation to fly in space.
“We have doubled the number of nationalities onboard the space station, going from four to eight, which I think is a great testament to the international collaboration which underpins this marvelous space station,” said Andreas Morgensen, current commander of the ISS crew.

NASA cracks asteroid container
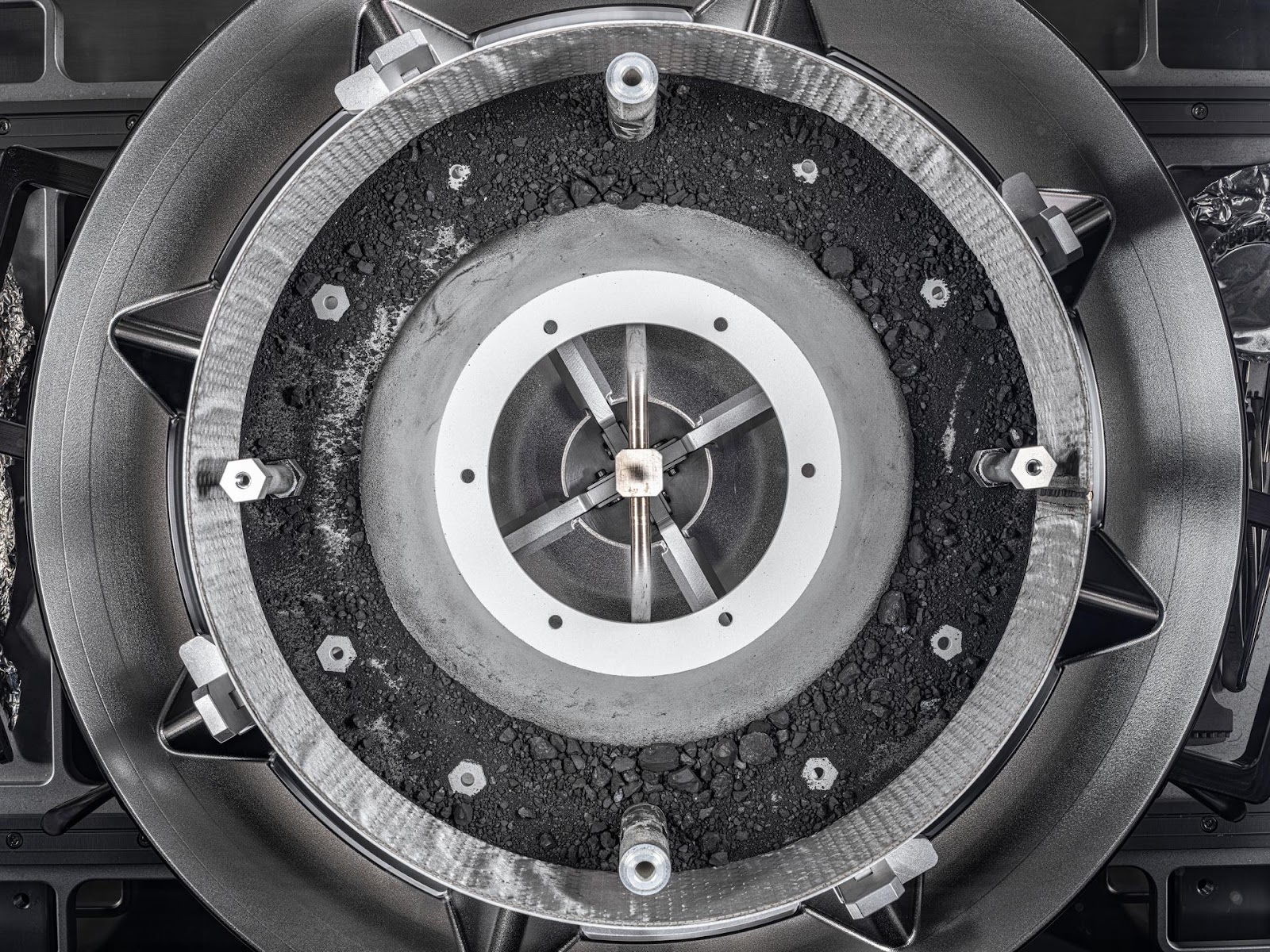
In September, the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft dropped a capsule containing bits of the asteroid Bennu onto a Utah desert, marking the successful conclusion of NASA’s first asteroid sample retrieval mission.
Actually getting the sample out of the capsule proved to be harder than NASA anticipated, though — two of the 35 fasteners on the container holding the sample couldn’t be removed using the equipment it had prepared for the task.
NASA was finally able to remove the stubborn fasteners using custom-built tools, and on January 19, it shared the first image of the hard-to-reach space rock.
“Our engineers and scientists have worked tirelessly behind the scenes for months to … design, develop, and test new tools that allowed us to move past this hurdle,” said Eileen Stansbery, division chief for ARES at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. “The innovation and dedication of this team has been remarkable. We are all excited to see the remaining treasure OSIRIS-REx holds.”
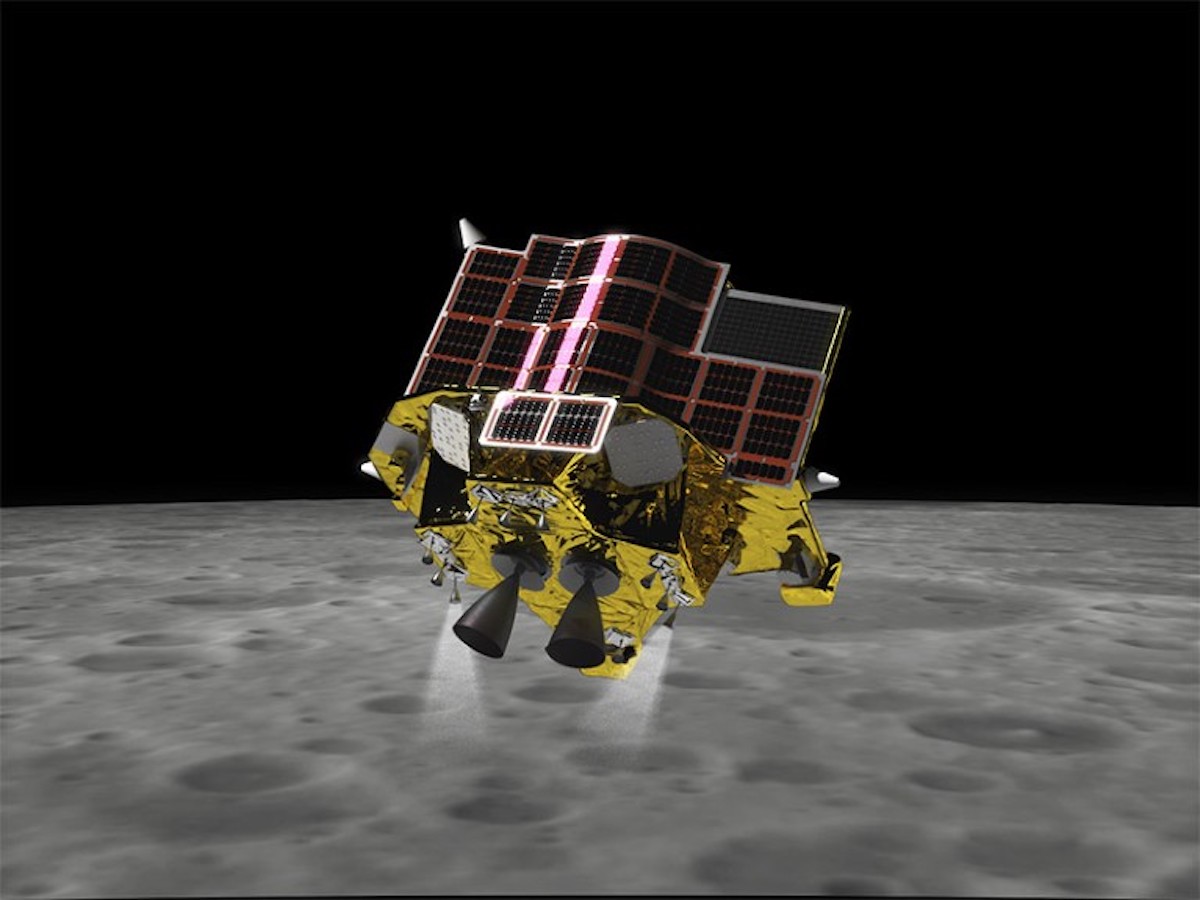


Japan lands on the moon
On January 19, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA’s) Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) spacecraft touched down on the moon. This made Japan just the fifth nation in history to successfully “soft land” on the lunar surface.
The spacecraft appeared to have trouble with its solar panels after the landing, though, meaning it was running strictly on battery power. When the battery was at 12% — about three hours after the historic landing — JAXA shut down the spacecraft.
JAXA will now analyze the mission data to see if it met its goal of landing SLIM within 100 meters of its target — because most moon missions measure accuracy in kilometers, this objective earned the mission the nickname “Moon Sniper.”
Japan’s space agency isn’t giving up on the possibility of SLIM reawakening at some point, either.
“If sunlight hits the moon from the west in the future, we believe there’s a possibility of power generation, and we’re currently preparing for restoration,” JAXA said in a statement.
We’d love to hear from you! If you have a comment about this article or if you have a tip for a future Freethink story, please email us at [email protected].