How long does it take toxic “forever chemicals” to break down? It’s a trick question, because as their nickname suggests, they don’t break down … at least not for hundreds or potentially thousands of years.
However, researchers from the University of British Columbia (UBC) have developed a new water treatment that filters and removes harmful forever chemicals – or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) to use their proper name – from drinking water, safely, efficiently and permanently.
Where do PFAS come from?
You can’t see them with the naked eye. But with more than 4,700 substances in use, PFAS applications are more than likely in your home or workplace and often end up in the environment – specifically seeping into rainwater, soil, sediment and drinking water, where they can be ingested by humans and animals.
Industry has been using these manufactured chemicals since the 1940s: including to waterproof wet weather gear; make non-stick cookware non-stick; in stain-resistant fabrics and carpets; some cosmetics; firefighting foams; products that are manufactured to be grease-, water- or oil-resistant; fast-food packaging; household products like shampoo and dental floss… the list goes on.
The cost to society of PFAS has recently been estimated at $17.5 trillion annually, while the manufacturers themselves make $4 billion per year in profits, reported the Guardian.
How are PFAS removed from drinking water?
Lead scientist Dr Mohseni and his team at UBC have developed a unique silica-based material with a high capacity to absorb a range of PFAS from drinking water. The reusable material acts like a filter, trapping most of the harmful particles, which are then destroyed using unique electrochemical and photochemical processes developed by the researchers.
“Our absorbing media captures up to 99% of PFAS particles and can also be regenerated and potentially reused. This means that when we scrub off the PFAS from these materials, we do not end up with more highly toxic solid waste that will be another major environmental challenge,” said Dr Mohseni.
Separate research by scientists at Arizona State University in the US, uses microorganisms to break down PFAS.
Led by 2018 Stockholm Water Prize winner Bruce Rittmann, the team uses a specially modified membrane known as MCfR that causes a reaction in water, to attack the chemical composition of PFAS particles it contains. The water is then treated by microorganisms in a special reactor (MBfR) to break down the remaining pollutant particles, which possess among the strongest carbon bonds in chemistry.
“We use the MCfR to knock off a few to all of the fluorines, and then we hand that water with those compounds over to the microorganisms in the MBfR, and they finish the job,” said Rittmann.
What health impacts are associated with PFAS?
Most people come into contact with forever chemicals through food, consumer products or by drinking contaminated water. Exposure to PFAS has been linked to health problems such as liver damage, thyroid disease, obesity, fertility issues and cancer, according to the European Environment Agency.
Noxious particles from sprays, chemicals and treatments accumulate over time and can end up polluting waterways or being absorbed into the body from using certain cosmetics.
While PFAS are no longer used by manufacturers in countries like Canada, where the research was conducted, they are still found in various products.
Across the border, most people in the US have been exposed to PFAS and have traces of the pollutants in their blood, according to the Agency for Toxic Substance and Disease Registry (ATSDR).
Blood levels of the most common PFAS in people in the US over time
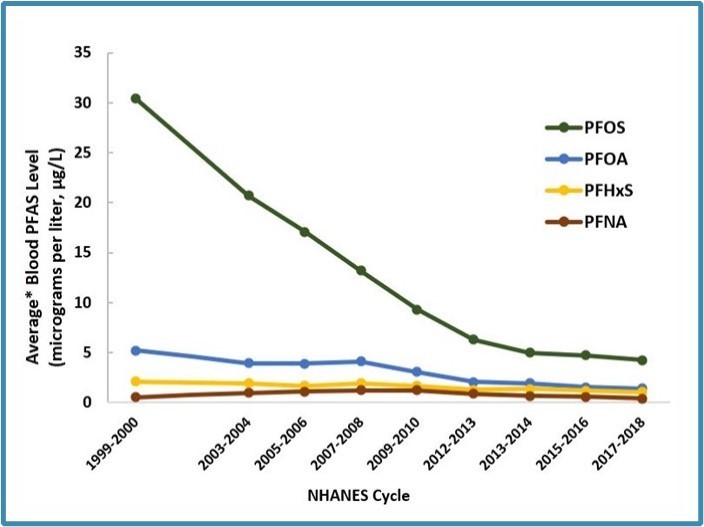
However, the use of the most common types of forever chemicals has declined in the US, with tests of contamination levels in the blood of people in the US showing forever chemicals like PFOS levels have declined by more than 85%, and PFOA levels by more than 70% during the first two decades of the century.
But as the main PFAS chemicals are phased out, they may be replaced by others that leave people exposed to health risks, the ATSDR notes.
Countries to enforce legislation on forever chemicals
Contaminants like forever chemicals are symptomatic of the wider pollution and environmental breakdown harming the planet.
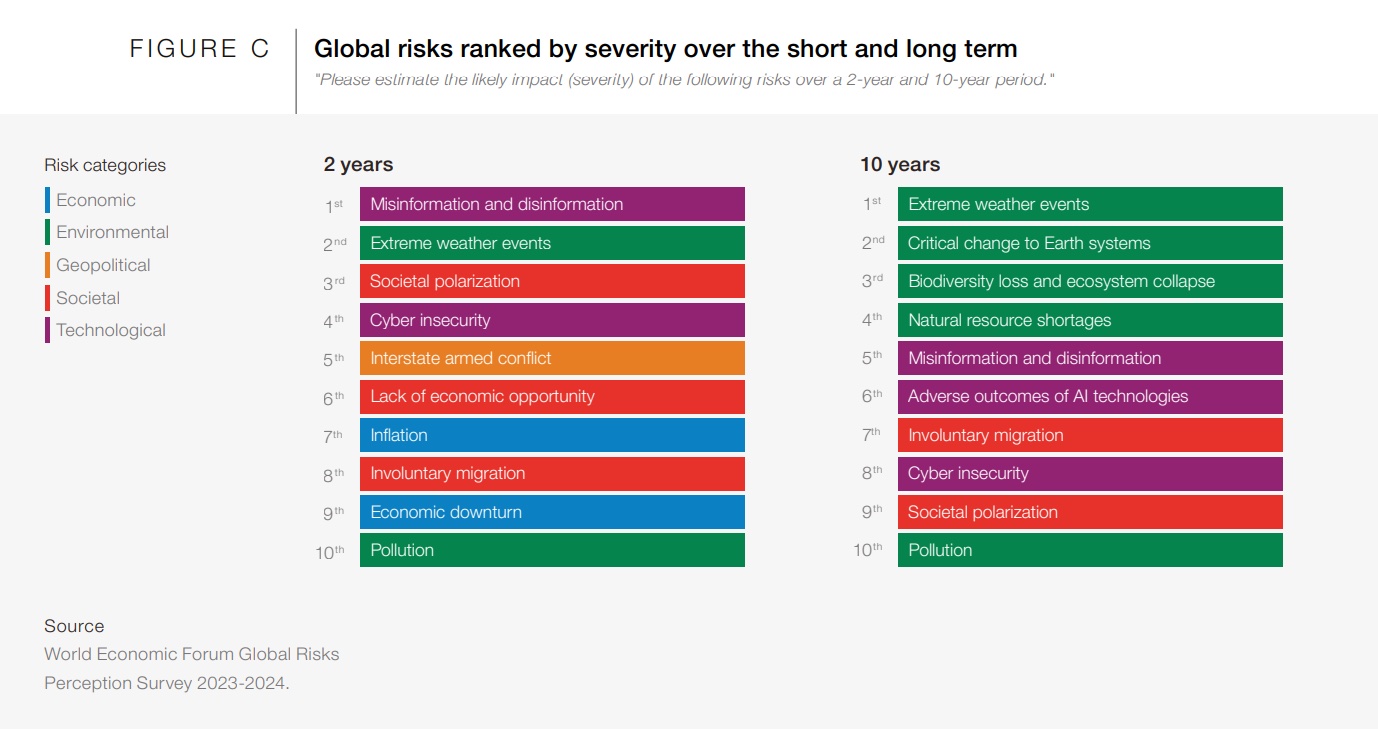
The World Economic Forum’s Global Risks Report 2024 lists pollution as the 10th most pressing threat to society, both in the short and long term.
Meanwhile, biodiversity loss and ecosystem collapse are ranked third in the top-10 list of perceived threats in the next 10 years.
Responding to the damage caused by pollutants, the US Federal government has set national limits on levels of toxic PFAS in drinking water, reports Smithsonian Magazine. Under the legislation, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has imposed a limit of four parts per trillion for two types of PFAS: PFOA and PFOS. Four other regulated compounds – PFNA, PFHxS, PFBS and “GenX chemicals” – have individual limits imposed on their use.
Water providers in the US will have a three-year period to conduct tests and if the results show levels of PFAS chemicals in drinking water that exceed the specified levels, they will have two further years to install treatment systems to remove these toxins.
The EU and other countries are set to enforce legislation to restrict the widespread use of PFAS.
This article is republished from the World Economic Forum under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.






