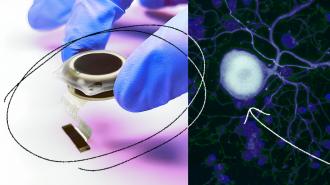
Neuralink, Elon Musk’s neurotechnology company, has implanted its first device in a human patient, according to posts on X by Musk.
The device, called Telepathy, is a brain-computer interface (BCI) designed to allow users to directly control computers and phones with pure thought. The initial use case for the device will be to assist people who have lost the use of their limbs, and it could one day be revolutionary for conditions that block speech.
“Imagine if Stephen Hawking could communicate faster than a speed typist or auctioneer,” Musk said on X.
Musk wrote that the patient is “recovering well,” and the device is showing promising signs of neuron spike detection: the recording and decoding of electrical impulses generated by individual neurons. Not much is publicly known about the Telepathy device’s capabilities. Still, Neuralink had previously disclosed that each of the device’s 64 neural threads, the super-thin wires on its coin-sized BCI, contained 16 electrodes, bringing the total electrode count per device to 1024.
The device may have been implanted using a surgical robot that Musk unveiled at a Neuralink presentation in August 2020. This unnamed surgical robot has three main components: a helmet-shaped head that holds the patient’s head in place during surgery, a humped-shaped body that contains parts responsible for the movement of the device, and a base that contains computing resources for the bot.
In May 2023, Neuralink received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration to proceed with clinical trials of its implant, then nicknamed “the Link,” as well as the surgical robot. The approval to proceed with human trials came after the company was initially denied its application due to safety concerns about the device’s components potentially impacting other parts of the brain and potentially causing brain damage when removed.
Neuralink’s trial, PRIME (Precise Robotically Implanted Brain-Computer Interface), will last six years and is focused on testing its implant for patients with quadriplegia. Patients will undergo an 18-month study with follow-up care over 3.5 years.
If early safety and efficacy trials are successful, Neuralink aims to use its BCIs for various medical applications, including restoring vision, motor function, and speech. However, Neuralink’s long-term vision extends beyond medical applications. The company eventually hopes to achieve broader implementation of BCIs — even among people without disabilities. Musk has speculated that BCIs could someday expand the power of human cognition and enable people to “achieve a kind of symbiosis with artificial intelligence.”
Neuralink is far from the first company to utilize implantable BCIs in human patients. In 2017, Freethink profiled Ian Burkhart, who was implanted with the NeuroLife System developed by Battelle Memorial Institute and the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. Synchron, BrainGate, and Paradromics are also developing BCIs and are conducting human clinical trials for their respective BCI devices.
We’d love to hear from you! If you have a comment about this article or if you have a tip for a future Freethink story, please email us at [email protected].