Field: Medicine
Low doses of nitrous oxide may treat depression
A new, small study has found that low doses of nitrous oxide — laughing gas — can treat symptoms of depression.
MIT researchers can fit more drug in less pill
A new drug formulation method developed by chemical engineers at MIT can fit more drug into less pill.
Beer hops could hold key to preventing common liver disease
Compounds derived from hops might be able to help prevent — or even treat — nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in people.
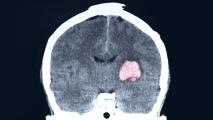
Two opposite kinds of stroke. One promising treatment.
A new stroke treatment could give doctors a way to help victims sooner, improving their chances of avoiding permanent brain damage.
Hope and controversy: FDA approves first new Alzheimer's drug in decades
The FDA has approved the first new Alzheimer’s drug in decades, but the decision brings not only hope, but controversy.
Blood test can quickly tell if a targeted cancer therapy works
The ExoSCOPE blood test can determine with 95% accuracy whether a targeted cancer therapy is working within 24 hours of administration.
"Light-shrinking" material cranks normal microscopes up to 11
Researchers have developed a light-shrinking slide coating that allows light microscopes to image in “super-resolution.”
Inhaled nanobodies treat COVID-19 in hamsters
An inhaled nanobody treatment for COVID-19 has shown promise in animal tests and could be a more affordable alternative to monoclonal antibody drugs.
Robot paramedics are bringing mechanical CPR to the UK
An English ambulance service has begun using robot paramedics to deliver mechanical CPR to patients.
The first steps towards an allergic asthma vaccine
French researchers have shown an allergic asthma vaccine to be effective in mice. The next step: human clinical trials.
Can new drugs make obesity a medical — not moral — condition?
Researchers are hopeful that a class of drugs called incretins will not only treat obesity, but help people think of it as a medical condition.
These glowing bacteria can diagnose gut problems
Using synthetic biology, a team at Rice has designed bacteria that can sense signs of inflammatory bowel disease in mice.
Molecular "tweezers" pick apart bacterias' biofilm
Israeli researchers have developed a set of “molecular tweezers” that can pick apart the biofilm which protects some bacteria.
Gene therapy appears to cure “bubble boy disease”
A new gene therapy designed to treat children with ADA-SCID, a form of “bubble boy disease,” was incredibly successful in trials.
How a smartphone app is helping suppress HIV
An HIV app that uses gaming elements to motivate people to stick to their ART regimen was able to increase viral suppression in a small study.
3D-printed nose cartilage may someday fix your face
Researchers have developed a way to bioprint nose cartilage that they hope will one day minimize the need for invasive harvesting from the ribs.
Icy microneedle patch delivers cell therapy, then melts
A new microneedle patch features needles made of ice instead of traditional materials, making it suitable for cell therapy delivery.
Oxford malaria vaccine is 77% effective in young children
A malaria vaccine developed by Oxford University was 77% effective at protecting children during a phase 2 trial in Africa.
Weekly insulin shots may be “game-changer” for diabetes
Daily insulin injections can be burdensome and stigmatized. New clinical trials suggest a weekly insulin regimen can work just as well.
A modified herpes virus can fight brain cancer in children
In a small clinical trial, using herpes viruses modified to only infect tumors — oncolytic virus therapy — more than doubled the life expectancy of children with aggressive brain tumors.
Inhaled asthma drug accelerates COVID-19 recovery at home
Budesonide — a cheap, inhaled asthma drug that can be self-administered — appears to shorten at-risk COVID-19 patients’ recovery times.
Phone cameras can now measure your pulse and breathing
A team of researchers has developed an algorithm to measure pulse and respiration rate during a telehealth appointment using your device’s camera.
New oral insulin tech replaces needles with nanoparticles
If the success of a new oral insulin delivery system in rats translates to people, it could entice more diabetics to pursue insulin therapy.
Penn scientists correct genetic blindness with a single injection into the eye
Antisense oligonucleotide therapy uses small molecules to alter RNA. Researchers have now used those molecules to alleviate a genetic form of blindness.
Nobel prize-winning chemist helps invent synthetic mucus
Mucins, the long proteins in mucus, have an array of bacteria-fighting properties. These artificial mucins can act like the real thing.
Injectable “glue” helps heal traumatic brain injury in rats
By injecting a “brain glue” into rats, researchers were able to speed up their recovery after a traumatic brain injury.
New cancer treatment uses “hot blood cells” to target tumors
A new cancer treatment combining immunotherapy, photothermal therapy, and modified blood cells was highly effective in mice.
Scientists have created a heart valve implant that grows
Children may have heart valve replacement surgery 5 or more times. A lab-grown, growing valve may change that in the future.
IBM’s artificial intelligence may help us defeat superbugs
A new AI tool detected 20 viable drug candidates in less than two months
New drugs are taking the fight to lung cancer
KRAS mutation, which causes tumors to form, was long considered “undruggable.” But new drugs could be approved by year’s end.
Duke scientists find a potential vaccine for UTI
Despite being common, painful, and persistent, there’s currently no vaccine treatment for UTIs. But a new method has shown promise in mice.
Can RNA create a malaria vaccine?
An effective malaria vaccine could save hundreds of thousands of lives each year. Can RNA vaccines like the ones fighting SARs-CoV-2 tackle another disease?
Radioactive bone cement may help treat spinal tumors
External radiation can damage bones and cause side effects. Radioactive bone cement directly into the spine may be a better option.
Diabetes drug shows promise as obesity treatment
The diabetes drug semaglutide shows promise as an obesity treatment, helping people lose an average of 34 pounds in a recent trial.
Study: Strong immunity without Pfizer vaccine’s second dose
The Pfizer vaccine's second dose might not be as necessary as thought — and ultra-cold storage of the COVID-19 vaccine might not be necessary at all.
Fecal transplants help shrink cancer patients’ tumors
Fecal transplants made advanced melanoma patients who initially didn’t respond to immune checkpoint inhibitors responsive to the cancer treatment.
Biologist infects himself with parasites in pursuit of hookworm vaccine
A marine biologist intentionally infected himself with parasitic hookworms and documented it in Tweets and pictures that will make your skin crawl.
Trees and insects helped create Novavax’s COVID-19 vaccine
Novavax’s COVID-19 vaccine was nearly 90% effective in a U.K. trial — and the ingredients for the promising subunit vaccine came from insects and trees.
HIV drugs appear to prevent the #1 cause of vision loss in seniors
An HIV drug appears to prevent dry macular degeneration, suggesting that drug repurposing could be a viable strategy for treating the incurable disease.
Designer DNA hunts down multiple myeloma in mice
Researchers have developed designer DNA that kills cancer stem cells at their roots, showing early signs of success preventing relapse in mice.
Personalized skin cancer vaccine is made from tumor cells
A personalized skin cancer vaccine developed from melanoma survivors’ own tumor cells has shown promise in a small trial.
This robot creates a GPS for your lungs
In partnership with Intuitive
A traditional lung biopsy is incredibly invasive, but new tech is allowing doctors to get ahead of lung cancer and give patients a fighting chance.
Stomach implant tells your brain you're not hungry
A tiny implant uses LED light stimulation to stave off hunger, offering a new weight loss option, and gastric bypass alternative, for people suffering from obesity.
Smart vape pen claims to solve the cannabis dosing problem
To solve the cannabis dosing problem, the MODE smart vape vibrates when a person should stop inhaling and again when they should exhale.
Phage therapy kills superbug behind many ICU infections
Combining a bacteria-killing virus and an antibiotic was able to wipe out an infection of the superbug A. baumannii in mice.
Cancer cells can hibernate to escape chemotherapy
A new study has found evidence that cancer cells hibernate, slowing down their division and waiting out the harsh environment of chemotherapy.
These brain implants can predict an epileptic seizure days in advance
For the first time, a study has shown that brain activity could be used to forecast the onset of epileptic seizures several days in advance.
A cancer immunotherapy technique may prevent diabetes
Engineered immune cells can fight off rogue T cells which damage the pancreas and cause type 1 diabetes.
These are the medical breakthroughs that inspired us in 2020
2020 has put medicine to the forefront like never before. Freethink’s B. David Zarley looked back on the year and chose three medical developments that inspired him.
Genetically engineered tomato can grow drug to treat Parkinson’s
The latest biopharmaceutical is a drug for Parkinson’s disease, Levodopa, produced by genetically modified tomato plants.
4 people in the world have a mysterious dementia. Could it hold a key to Alzheimer’s?
Alzheimer’s has proved difficult to treat. But solving the mystery of this ultra-rare frontotemporal dementia may unlock new understanding.
New pancreatic cancer treatment penetrates tough tumors
For a new pancreatic cancer treatment, researchers attached a chemotherapy drug to an antibody that targets a molecule on the outside of cancer cells.
Cancer immunotherapy “baits” the immune system into attacking hidden lung tumors
When cancer spreads, it often ends up in the lungs. ImmunoBait can ride a red blood cell in mice to deliver cancer immunotherapy where they live.
New skin cancer vaccine is twice as powerful
By adding two “boosters” to an in-development skin cancer vaccine, scientists may have improved its ability to prevent melanoma recurrence.
New vanishing wound dressing heals skin with minimal scarring
A new kind of hydrogel dressing improves wound healing and minimizes scarring by kicking the adaptive immune system into gear.
Finally! A smart toilet offers fecal testing for the masses
Fecal testing can reveal a surprising amount of medical data. Israeli startup OutSense wants to do so from your home.
Psilocybin therapy appears to dramatically reduce depression
Psilocybin therapy — a combination of traditional therapy and supervised “trips” on the magic mushroom compound — shows promise as a depression treatment.
New nano drug may be able to break drug-resistant cancers — with fewer side effects
Drug-resistant cancers reduce the effectiveness of chemo. A team of researchers may have found a potential way to treat them.
Are fecal transplants the fountain of youth?
Scientists hope that fecal transplants from younger to older people could be used to treat age-related cognitive decline.
15-minute blood test reveals the severity of traumatic brain injury
Researchers have now designed a rapid blood test that can help identify the severity of a brain injury in just fifteen minutes.
A new molecule may take the edge off vaccines — and make them perform better
Adjuvants create a better vaccine immune response, but they also cause inflammation. A peptide may help curb their side effects while improving protection.
Symptoms of Parkinson's are the only way to diagnose it. But not for long.
Researchers discovered a new way to diagnose and track Parkinson's disease progression — even before the first symptoms of Parkinson's appear.
“Google Maps for the human body” offers a deep view inside our trillions of cells
Researchers are creating an interactive, 3D map of the human body to help identify and prevent disease.
The future of vaccines may be injectable gels
Scientists have designed a slow-releasing vaccine that can more accurately match the timeframe of a natural infection.
Could a single injection send diabetes into remission?
Research has found that a single surgical injection of a protein into the brain can restore blood sugar levels and send diabetes into remission, for rodents. This could transform the lives of people living with diabetes.
$25 genetic test can improve asthma treatment for kids
Before prescribing an asthma treatment to children, doctors should use a cheap genetic test to look for a specific altered gene, according to a new study.
New ALS treatment appears to slow disease progression
A new ALS treatment that appears to slow disease progression offers hope to those battling the incurable neurological disorder.
Weird, synthetic intestinal lining could make treating diseases easier
A synthetic intestinal lining could make it easier for doctors to control drug delivery and nutrient absorption in patients.
Robots are running COVID-19 drug development
IBM’s new online platform, RoboRXN, combines artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and robotics to automate the COVID-19 drug development process.
Redesigned syringe could increase global access to medicine
A double-barrel syringe developed at MIT makes it possible to inject highly viscous biologics, making them more accessible to patients.
“Antivitamins” could be the cure for antibiotic resistance
The B1 antivitamin helps bacteria kill competing bacteria, leading researchers to suspect it could help us fight antibiotic resistance and superbugs.
Doctors spray chemo inside abdominal cancer patients
For the first time, a U.S. trial will test the ability of an experimental cancer treatment called PIPAC to help late-stage abdominal cancer patients.
Immune proteins show promise as COVID-19 treatment
Immune proteins called interferons appear useful as a COVID-19 treatment if given to patients before an infection becomes severe.
Urine test could replace malignant melanoma biopsies
Doctors can look to the levels of certain fluorescent molecules in the urine of malignant melanoma patients to track the progression of their skin cancer.
Researchers create blueprint for the “love hormone” receptor
The shape of the love hormone receptor is finally revealed in a 3D map created by researchers at the University of Zurich.
Medieval medicine yields modern weapons
Deadly antibiotic-resistant superbugs require new weapons. Ancient and medieval medicine may point us to where to find them.
Designer antibodies could help treat and prevent COVID-19
A pair of new trials will test the ability of designer antibodies to not only treat COVID-19, but also potentially prevent coronavirus infections.
Human-like "organ chips" could eliminate animal studies
To rapidly test for COVID-19 treatments without animal studies, researchers make a model human body out of “organ chips.”
Study: blood transfusions can slow signs of aging in mice
A new study shows that blood from fitter mice can reverse cognitive decline in sedentary mice.
For the first time, researchers edit human mitochondrial DNA
Researchers can now edit a part of the human genome that CRISPR has never been able to. This opens up new possibilities for research and cures for devastating rare genetic diseases.
Researchers heal human lungs by hooking them up to live pigs
In a remarkable experiment, researchers heal human lungs by connecting them to live pigs. And the pigs are unscathed.
Microdosing marijuana can relieve chronic pain
Microdosing marijuana can relieve chronic pain without impairing a person’s ability to think clearly, according to a new study.
Researchers discover how to improve eyesight naturally
The world is aging, and with age comes vision decline. New research may have found how to improve eyesight in an accessible way.
Nanotech endometriosis treatment could ease women’s pain
An in-development endometriosis treatment uses dye-filled nanoparticles to identify and destroy diseased tissues.
Building a factory for human organs
Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine experts are working to mass-produce human organs through the ARMI consortium.
Gene therapy hailed as cure for sickle cell disease
A gene therapy that uses CRISPR to edit a patient's own stem cells looks like a “functional” cure for sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia.
The first life-saving coronavirus drug is a common steroid
A large clinical trial in the U.K. identified the cheap, widely available steroid dexamethasone as potentially the first life-saving coronavirus drug.
First coronavirus antibody drug trial launches in us
An antibody drug developed to treat people with COVID-19 — and potentially prevent new infections — is now being tested in humans.
New drug could provide long-term HIV prevention
HIV prevention typically requires a daily pill. A new, injectable drug may be able to work for over a month at a time.
This ultrasound connects to an iPhone to help catch COVID-19
Ultrasound can be a useful diagnostic tool for COVID-19. A portable ultrasound machine called the Butterfly iQ may make it safer.
Children and seniors to join Oxford’s coronavirus vaccine trial
Oxford University is enrolling people older than 70 and children between the ages of 5 and 12 in a Phase 2 coronavirus vaccine trial.
New HIV vaccine gives monkeys longer-lasting protection
Scientists have created an HIV vaccine that triggers two types of immune response, providing monkeys with longer-lasting protection from infection.
CBD slows growth of brain cancer cells in a Petri dish
The cannabis compound CBD can slow the growth of brain cancer cells, but it’s a long way from a new cancer treatment.
Researchers are rushing to freeze… lab mice sperm?
With their labs closing and the future unclear, researchers are sending precious cargo — the sperm of lab mice — to be frozen and stored.
A proposal to infect volunteers, the race to a vaccine, and more COVID-19 updates
In our weekly news roundup, we take you inside the fight against COVID-19 to explore the solutions on the frontlines of an unprecedented global response.
Using Ebola to fight brain cancer
A lab-altered Ebola virus can hunt human brain cancer cells without killing healthy cells.
Oxford coronavirus vaccine could be ready by September
Millions of doses of an Oxford coronavirus vaccine now in the human trial stage could be ready by September, according to researchers.
An “old school” COVID-19 vaccine appears to work in monkeys
An in-development COVID-19 vaccine has protected animals from catching the novel coronavirus for the first time, according to the team behind it.
Would you volunteer to be infected with COVID-19?
Coronavirus vaccine development could take months. There’s a potential shortcut though: purposefully exposing research subjects to the virus.
At-home test kits, new vaccine developments, and more COVID-19 updates
In our weekly news roundup, we take you inside the fight against COVID-19 to explore the solutions on the frontlines of an unprecedented global response.