Field: Medicine
Psychedelics, brain implants, and the future of chronic pain relief
The future of chronic pain relief could include psychedelics, gene therapies, brain implants, and other cutting-edge alternatives to opioids.
MIT’s new bacteria protects guts from antibiotic-caused dysbiosis
An engineered bacteria protects the gut microbiome from antibiotics to help people battle infections without risking dysbiosis.
Probiotic gut bacteria can produce a vital Parkinson’s drug
L-DOPA is a miraculous Parkinson’s drug with terrible side effects. Researchers have created drug-producing bacteria that may help.
Strange treatment may restore sense of smell after COVID
Philadelphia doctors are treating COVID patient’s loss of smell with plasma-soaked sponges. But whether it is working or not still needs to be sniffed out.
A common arthritis drug treats alopecia (Updated)
A common arthritis drug may be an effective alopecia treatment, based on a trial in which it helped people regrow their hair in just 36 weeks.
Rare double lung transplant saves cancer patient’s life
A Chicago lung cancer patient’s successful double lung transplant is a ray of hope for others with the deadly disease.
Wounds of kids with “butterfly disease” healed by DNA gel
A topical gene therapy helped heal the wounds of people with “butterfly disease,” a painful disorder that makes the skin incredibly fragile.
Reversing hearing loss with regenerative therapy
MIT spinout Frequency Therapeutics’ drug candidate stimulates the growth of hair cells in the inner ear.
Cancer is addicted to iron. It could be a fatal weakness.
By homing in on the high levels of iron in certain cancer cells, researchers have created a more targeted anticancer drug.
How tattoo machines could revolutionize vaccination
A tattoo machine may be a better delivery method for DNA vaccines than the standard syringe and hypodermic needle.
Male birth control pill to enter human trials in 2022
Clinical trials of a male birth control pill that was 99% effective at preventing pregnancy in mice are expected to launch in 2022.
Vaccine used to treat COVID-19 for first time
A man whose persistent coronavirus infection kept him isolated for 7 months finally tested negative after receiving a COVID-19 vaccine.
Space lettuce engineered to stimulate bone growth
To protect Mars astronauts from bone loss, scientists genetically engineered a lettuce that produces a bone-stimulating hormone.
Michio Kaku makes 3 predictions about the future
Dr. Michio Kaku on what is likely and what is possible provides a stimulating vision of the future.
New children’s malaria treatment clears out infection in liver
Malaria can hide in the liver, causing relapse months or years later. Now, public health officials have a new treatment to prevent relapse for children under 16.
One shot of this COVID-19 drug reduces risk of death by 60%
In-development COVID-19 drug Peginterferon Lambda reduced risk of hospitalization or lengthy emergency room visits by 50% in a phase 3 trial.
New Ebola antibodies neutralize the most dangerous strains of the virus
Researchers have found two new antibodies which bind to the most dangerous strains of Ebola.
Safer painkillers: A novel drug treats pain without killing people
Painkillers have nasty side effects, such as organ damage or addiction. Researchers have discovered a new drug that may cause none of these.
Anti-aging isn’t a scam, but immortality almost certainly is
A new biotech firm with $3 billion in funding has announced plans to combat aging. But what does that mean for human life span, exactly?
Clues to schizophrenia and bipolar disorder hidden in the dark genome
A new study suggests that the causes of these disorders are hidden in "dark genes," which may account for the enigma of their development.
Moderna will develop mRNA vaccines for Ebola, malaria, other major threats
Moderna is developing mRNA vaccines for 15 “priority" pathogens and launching a program giving other developers access to its mRNA tech.
How the antidepressant Prozac could treat blindness
Prozac is a widely used antidepressant. Data indicates that the drug could be used to prevent blindness due to macular degeneration.
New antidepressant helps patients in just three days
Adding the new antidepressant zuranolone to standard treatments helped people with major depressive disorder feel better in less time.
90% of drugs fail clinical trials – here’s one way researchers can select better drug candidates
It’s disappointing when the years of effort and resources spent to push a drug candidate to patients so often lead to failure.
What the Russian invasion means for clinical trials in Ukraine
Russia’s invasion has the potential to disrupt clinical trials in Ukraine, warns one of the many companies staging trials in the nation.
How mRNA and DNA vaccines could treat autoimmune disorders, genetic diseases, and more
Using DNA or an mRNA vaccine, researchers are investigating the feasibility of essentially replacing missing genes that cause disease.
How close are we to curing blindness?
New approaches to curing blindness are heralding a future in which fewer people have to live life completely in the dark.
Despite its disastrous effects, COVID-19 offers some gifts to medicine
While it’s still too early to draw conclusions, there's emerging evidence between autoimmune disorders and the virus that causes COVID-19.
Opioid overdose: A bioethicist explains why restricting supply may not be the right solution
Since the unpredictability of drug supply increases overdose risk, making the drug supply predictable should be part of the solution, right?
Insulin pump can be controlled with an app
A new app lets insulin pump users deliver doses remotely, making it easier to manage diabetes discretely and conveniently
Horseshoe crabs are drained for their blue blood. That practice will soon be over.
One of humanity’s strangest and most macabre activities is slowly coming to an end, a trend that every horseshoe crab should celebrate.
Golden blood: The rarest blood type in the world
Golden blood, despite sounding like medical nonsense, is actually the nickname for Rh-null, the world’s rarest blood type.
First gene therapy for Tay-Sachs disease successfully given to two children
After 14 years in development, gene therapy has helped two children surpassed their life expectations and live seizure-free.
New antibody treatment against Omicron gets emergency approval
A new monoclonal antibody treatment effective against Omicron has received emergency authorization weeks after two others were banned.
First woman cured of HIV through stem cell transplant
A woman has been cured of HIV through a transplant of umbilical cord blood, which is easier to match to patients than bone marrow.
Monkeys’ alcohol consumption drops 50% after hormone therapy
Heavy-drinking monkeys cut their alcohol consumption by 50% after researchers treated them with a hormone called “FGF21.”
Coffee mug company builds high-tech box to keep vaccines cold
Smart mug company Ember has created a shipping container to help bolster the medicine cold chain.
MIT tests pill to deliver RNA vaccines and therapies
A tortoise-inspired capsule designed by MIT can deliver RNA vaccines and other nucleic acid therapeutics without injections.
Cataract surgery associated with lower risk of dementia
In a new study of thousands of patients, those who had cataract surgery had a reduction in dementia risk.
Gene therapy shows promise at treating severe form of epilepsy
A new Dravet syndrome treatment that targets genes could help extend the lives of people with the rare, but severe form of epilepsy.
Mark Cuban launches online pharmacy to cut drug prices
Billionaire investor Mark Cuban has launched an online pharmacy designed to cut the cost of generic drugs by as much as 99%.
Morning glories may be a source of new psychedelics and medicines
Researchers have found that the symbiotic relationship between a fungus and a morning glory holds the potential for new psychedelic compounds and medicines.
Researchers find a new target for a universal flu vaccine: the “anchor”
There’s a new target in the battle for a universal flu vaccine: the "anchor,” a part of the virus’ proteins less likely to mutate.
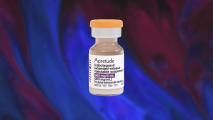
HIV prevention injection approved by FDA
The FDA has approved Apretude, an HIV prevention injection that replaces daily PrEP pills with a single shot every 60 days.
This robotics lab wants to develop the dream surgery
Chicago’s Surgical Innovation Training Lab is developing the robots, surgeons, and digital surgeries of the future.
5 clinical trials may bring new hope in 2022
Vaccines, gene therapies, and even an anti-aging pill: These are the clinical trial results we are looking forward to in 2022.
Teaching your immune system to ignore invaders
Autoimmune disorders can attack treatments. Can "reverse vaccination" keep the body at bay when necessary?
Google rolls out new tools to help your doctor search
Google has debuted new ways to make your doctor search easier, allowing you to know what insurance they take and languages they speak.
A chemical in grape seeds extends lives of mice by 9%
A chemical in grape seeds extended the lives of old mice, made young ones healthier, and helped chemo drugs shrink tumors in a new study.
First person cured of type 1 diabetes thanks to stem cells
An experimental stem cell treatment has eliminated type 1 diabetes in a patient, giving experts guarded hope for a diabetes cure.
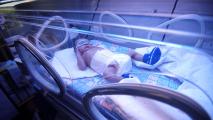
A simple webcam can automatically catch — and treat — infant jaundice
Researchers in Australia and Iraq have developed a system that uses a webcam to catch infant jaundice and begin treatment right away.
Genetically modified worms sniff out cancer in urine
Genetically modified worms that react to the scent of cancer in urine could one day be used for routine pancreatic cancer screening.
Tuberculosis may spread through aerosols, without coughing
University of Cape Town researchers believe tuberculosis may spread in small aerosols, much like COVID-19.
This engineer fixed his own heart
When Tal Golesworthy was told he was at risk of his aorta bursting, he wasn’t impressed with the surgery on offer – so he came up with his own idea.
How a BBQ lighter can make DNA vaccines more powerful
Georgia Tech researchers turned a BBQ lighter into a delivery system that uses electricity to boost the potency of DNA vaccines.
Second patient clears own body of HIV, hinting cure is possible
Two “elite controllers” that no longer have any replicable HIV virus in their bodies may hold the key to a cure for HIV.
“Dancing” molecules repair spinal cord injuries in paralyzed mice
A treatment for spinal cord injuries was able to reverse paralysis in mice by “dancing” to connect with cells near the site of the injury.
DeepMind’s AI lights path to faster drug development
Alphabet has announced the launch of Isomorphic Labs, an AI-driven drug discovery company built on research from its DeepMind subsidiary.
Pfizer’s antiviral pill cuts COVID-19 hospitalization, death by 89%
Pfizer’s antiviral pill to treat COVID-19 cut the risk of hospitalization or death by 89%, according to early results from a phase 2/3 trial.
A new clue in why oral vaccines don’t work as well in developing countries
Oral vaccines are crucial to public health, but work worse where they are needed most. A new mouse study has a potential reason why.
Preventative breast cancer vaccine enters human trials
A breast cancer vaccine entering human trials is designed to prevent triple-negative breast cancer — the deadliest, most aggressive form.
Merck is making its COVID-19 antiviral pill more affordable to low-income countries
Drug maker Merck has agreed to license a promising antiviral pill to treat COVID-19 to low- and middle-income countries for free.
Cooling caps can help prevent chemo hair loss
Chemo hair loss is a common side effect for cancer patients, but cooling caps can help limit the loss.
HIV treatment gets green light for human trials
Excision BioTherapeutics is cleared to begin human trials of a CRISPR-based HIV treatment that’s administered in just one IV infusion.
Johns Hopkins receives the first NIH grant for clinical psychedelic research in half a century
For the first time in decades, the National Institutes of Health is funding a clinical psychedelic study, perhaps a turning point for the field.
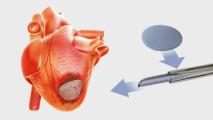
New cardiac patch can be implanted with a syringe
A new cardiac patch developed by Canadian scientists could help repair heart damage by supporting tissue without blocking electrical activity.
WHO recommends its first malaria vaccine
A malaria vaccine developed by GlaxoSmithKline, Mosquirix, has been recommended for use by the World Health Organization.
Pill to treat COVID-19 cuts risk of hospitalization or death in half
A pill to treat COVID-19 that cut hospitalizations and deaths in half could become the first oral medication against the disease.
Antiviral reduces COVID-19 hospitalizations by 87%
The FDA-approved antiviral drug remdesivir prevents high-risk people from ending up in the hospital, if given early.
A malaria antibody prevented infections in purposefully-infected volunteers
In a small study, researchers found an antibody that prevents malaria infection in people purposefully infected with the parasite.
Johns Hopkins has developed a lung cancer blood test
Researchers at Johns Hopkins are using AI to power a lung cancer blood test.
Want better nasal vaccines? Look to the bacteria in your nose.
Researchers are investigating the link between the bacteria inside your nose and how effective nasal vaccines can be.
mRNA cancer treatment shrinks tumors in mice
An mRNA cancer treatment in human trials has proven incredibly effective in mice, shrinking tumors in 85% of the rodents tested.
This implanted microchip may one day control your sleep
An implantable, wireless device could be better than popping a pill.
UK researchers are growing the Delta variant for human challenge trials
Responding to the variant’s rise, UK researchers are growing the Delta variant for trials.
A blood test for your circadian clock
Your circadian clock controls more than when you sleep and wake. Researchers are developing a simple blood test to try and accurately tell your time.
One antibody stops all strains of COVID-19 from infecting cells
A newly discovered antibody can neutralize all strains of COVID-19 and every other sarbecovirus known to infect humans.
Antibody cocktail highly effective at preventing COVID-19
An antibody cocktail developed by biopharmaceutical company AstraZeneca was highly effective at preventing symptomatic COVID-19 infections.
Tiny magnetic beads and turkeys may lead to better prosthetic limbs
MIT and Brown researchers have developed a technique using implanted magnetic beads that they hope will lead to better control of prosthetic limbs.
Brain-wide gene editing may one day treat Alzheimer’s
Researchers have developed a brain-wide gene editing technique that treated Alzheimer’s disease in mice.
Researchers have 3D-printed an active tumor
Tel Aviv University researchers have 3D-printed an active glioblastoma tumor, potentially paving a way to better study the lethal brain cancer.
MIT has created an inflatable prosthetic hand
MIT researchers have created a soft, inflatable prosthetic hand that provides advanced abilities at a fraction of the cost and weight.
Wasps inspire a new surgical needle
The next new surgical tool may come from an odd place: parasitic wasps whose eggs eat their hosts inside-out.
New organ coating could help prevent transplant rejection
A coating for donor organs that minimized the chance of transplant rejection in mice might one day eliminate the need for immunosuppressants.
Using body bags to treat heatstroke
The Pacific Northwest heat wave crushed hospitals with heatstroke victims. Doctors turned to body bags to save lives.
New treatment may prevent heart damage from COVID-19
An experimental drug that stopped the coronavirus from entering cells in heart organoids may be able to prevent heart damage from COVID-19.
Already-approved ALS drug may help Alzheimer’s patients
A small phase 2 study has found evidence that ALS medication riluzole may have potential as a drug for Alzheimer’s.
Inside your nose, it’s bacteria vs. bacteria in the fight against meningitis
Researchers have found that nose drops containing “friendly” bacteria can protect people against meningitis-causing bacteria.
New antibodies may lead to a norovirus vaccine
Researchers have discovered antibodies that neutralize a variety of norovirus strains, a possible step toward an effective norovirus vaccine.
Harvard has a vaccine against septic shock
A new vaccine platform based on biomaterial may eventually provide rapid protection against multiple bacterial threats.
This 3D-printed graft may improve ruptured eardrum surgery
Researchers at Harvard have developed a 3D-printed graft they hope will make ruptured eardrum surgeries safer, faster, and more effective.
FDA approves first drug to treat lymphoma in dogs
The FDA has approved a medication specifically designed to treat lymphoma in dogs, potentially helping extend the lives of thousands of pets.
Natural killer cells fight cancer without collateral damage
Researchers at McMaster have developed a form of immunotherapy capable of working on solid tumors in the lab.
Sky-mapping system can predict whether cancer treatment will work
Johns Hopkins researchers are using image analysis developed for astronomy to study cancer immunotherapy.
Pharma giant GSK embraces digital twins for vaccine development
Pharma leviathan GlaxoSmithKline is rolling out digital twins to help create “the vaccine factory of the future.”
CRISPR therapy cures first genetic disorder inside the body
For the first time, researchers appear to have effectively cured a genetic disorder by directly injecting a CRISPR therapy into patients’ bloodstreams.
Diagnosing infections without the lab — or wait
Researchers have developed a device that can test for infections in under an hour, no lab needed.
A new superbug strategy
Researchers at the University of Geneva have a new idea on how to stop superbugs: don’t kill them.
There may be a way to reverse acetaminophen damage in the liver
New research out of Singapore suggests that a protein thought to help acetaminophen toxicity may do the opposite.
Urine test for brain cancer detects tumors of any size
A new urine test for brain cancer analyzed microRNAs to correctly identify 100% of patients with brain tumors, regardless of their tumor’s size.