Field: Medicine
Scientists make pain relievers like Tylenol from pine trees rather than fossil fuels
Chemists have shown how to manufacture ibuprofen and acetaminophen using a waste product from the forestry and paper industries.
Weight-loss drug cut the risk of heart attack and stroke by 20% in large trial
The weight-loss drug semaglutide reduced patients’ risk of heart attacks, strokes, or death from heart disease by 20% in a large trial.
Fragile X syndrome often results from improperly processed genetic material
Researchers discovered that the mutated gene responsible for fragile X syndrome is active in most people with the disorder, not silenced.
Study finds tracking brain waves could reduce post-op complications
Researchers found brain wave signatures that could help determine when patients are transitioning into a deep state of unconsciousness.
Targeted therapy kills every type of cancer in the lab
City of Hope researchers are trialing a targeted therapy shown to kill more than 70 types of cancer in preclinical tests.
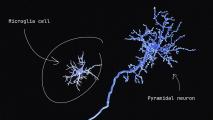
Immune cells in the brain may reduce damage during seizures and promote recovery
Microglia perform many functions in the brain, and their role in seizures is unclear — a new study in mice aims to find out more.
First-of-their-kind eye drops reverse blindness in teen
A topical gene therapy designed to heal the wounds of people with “butterfly skin disease” has now been used to reverse blindness.
New RSV shot protects babies against dangerous lung infections
The FDA has approved nirsevimab, an RSV shot that protects babies against the leading cause of infant hospitalizations in the US.
ADHD drugs could alleviate symptoms of Alzheimer’s
Scientists reviewed 40 years of clinical studies that assessed the effects of NA-targeting drugs, such as certain ADHD drugs, on Alzheimer’s.
Radioactive drugs are transforming cancer treatment
Radiopharmaceuticals allow doctors to directly target patients' cancer cells and avoid healthy tissue typically damaged by radiation therapy.
Not all repellents are equal – here’s how to avoid mosquito bites this summer
Researchers studied different types of mosquito repellents and their efficacy for over a decade. Here's what they found.
A functional cure for brittle diabetes is now available in the US
Islet transplantation, a procedure shown to functionally cure some people with hard-to-control brittle diabetes, has been approved in the US.
Drug to grow new teeth heads to human trials
A drug that causes animals to grow new teeth could one day allow us to regenerate teeth lost to injury, disease, or old age.
Newly identified type of depression affects 27% of patients
Stanford University researchers have identified a new, hard-to-treat type of depression characterized by problems with cognition.
AI-developed drug for deadly lung disease reaches phase 2 trials
AI-driven drug development has led to the launch of phase 2 trials of a drug to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
“Backdoor” into the ear offers new hope for reversing deafness
A new study has unlocked a “backdoor” into the inner ear that could make administering gene therapies to restore hearing less risky.
Certain diets can starve cancer cells
Low-calorie, intermittent-fasting, and ketogenic diets all can lower the amount of blood glucose available to fuel cancer cells.
A simple tweak could improve treatment of a deadly herpes brain infection
Anti-inflammatory drugs could potentially prevent herpes encephalitis from causing permanent brain damage.
Nasal drops might prevent PTSD
New research shows that nasal drops of neuropeptide Y triggers extinction of fear memories in an animal model of PTSD.
One shot epilepsy treatment reduced seizures by 95% in first two patients
A stem cell-based treatment for epilepsy slashed the number of seizures experienced by two trial participants by 95%.
Insulin grown in lettuce can be taken orally
New synthetic insulin harvested from lettuce plants can be made cheaply, taken orally, and transported at room temperature.
Cancer med appears to prevent brain aneurysms
Japanese researchers have discovered that the cancer drug sunitinib can prevent the formation of brain aneurysms in mice.
SpaceX successfully launches world’s first “space factory”
SpaceX has successfully deployed a “space factory” developed by startup Varda Space Industries to manufacture drugs in microgravity.
Cheap drug appears to cut long COVID risk by 41% in small study
The diabetes drug metformin cut COVID-19 patients’ risk of later developing long COVID by 41% in a small study.
90% of patients respond to new blood cancer treatment in trial
Israeli researchers have developed a new form of CAR-T therapy effective against multiple myeloma, a plasma cell cancer.
Made-to-fade tattoo ink keeps cancer therapy from leaving a mark
Henry Ford Health researchers are using temporary tattoo ink to help radiation therapy patients for whom permanent tattoos may not be an option.
New drug for fatty liver disease cuts fat by 65%
A new NASH treatment, efruxifermin, significantly reduced liver fat when combined with a GLP-1 drug in a small trial.
Lung cancer drug slashes patients’ risk of death by 51%
Osimertinib, an FDA-approved lung cancer drug, slashes the risk of death for certain patients by 51%, according to new trial results.
The placenta may play a role in the genetic risk of schizophrenia
Researchers at Johns Hopkins have found that genes associated with schizophrenia risk may impact the placenta, not just the brain.
Gain-of-function research is more than just tweaking risky viruses
Gain-of-function experiments in the lab can help researchers get ahead of viruses naturally gaining the ability to infect people in the wild.
Chronic pain can be objectively measured using brain signals
Even though pain is universal and we know it happens in the brain, we've never before had a way to objectively measure its intensity.
Do we finally know what causes Alzheimer’s?
The first treatments proven to slow cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s are helping settle a decades-long debate about how the disease starts.
This “bridge” between chemo and cancer solves a big problem for treatment
To improve leukemia treatment, Australian researchers have created a bispecific antibody that connects chemo drugs to cancer cells.
Cancer treatment is about to get a reboot, thanks to AI
Techniques borrowed from astrophysics are helping to advance personalized cancer treatments beyond what genetics can tell us.
Something found in bats could help us survive infections and inflammation
This protein may help bats survive viral infections and could be the springboard for new anti-inflammatory drugs.
Psychedelic inspires discovery of two new drug candidates for depression
Researchers have found ibogaine-inspired compounds effective in treating depression and addiction in mouse models.
First-in-US brain surgery performed in Boston
A surgical team has performed a surgery that alleviated a dangerous brain condition before it was too late.
Personalized mRNA vaccine preps the body to battle deadly cancer
A new pancreatic cancer vaccine based on mRNA tech was shown to be safe and capable of triggering an immune response in a small trial.
Potential way to treat anorexia found in microbiome
New research links the gut microbiome, an ecosystem of viruses, bacteria, and fungi, to the development of anorexia nervosa.
New gene therapy could reverse a common cause of blindness
A new study suggests we may be able to convert dormant eye cells into photoreceptors to reverse retinal degeneration.
Ultrasound could help us fight the deadliest cancer
In a small study, Northwestern researchers were able to get chemo drugs into the brains of glioblastoma patients with implanted ultrasound devices.
AI dramatically improved mRNA vaccines in just 11 minutes
A new AI tool can find the most stable mRNA sequence for a vaccine, leading to more effective shots that are less prone to degradation.
World’s first vaccine for RSV approved in the US
The FDA has approved the world’s first vaccine for RSV, a potentially deadly viral infection that has long eluded vaccination.
The first fecal transplant pill is heading to pharmacies
The FDA approval of the first fecal transplant pill could kick off an era in which we target the gut microbiome to treat many other diseases.
Complex brain activity detected in dying patients
Researchers have measured gamma waves, a sign of brain activity, in patients who were dying.
New Alzheimer’s drug slows cognitive decline by 35%
Eli Lilly’s new Alzheimer’s drug, donanemab, slowed cognitive decline by 35% in a phase 3 trial, but two people died from side effects.
Gene therapy reverses vision loss in primates — by making their eyes young again
A Harvard study found that a new gene therapy that reprograms cells to their younger state can reverse NAION-caused vision loss in primates.
New gel destroys brain cancer in 100% of treated mice
A new brain cancer treatment not only cured 100% of mice that received it, but also trained their immune systems to fight future cancers.
Two African countries first to approve Oxford’s malaria vaccine, with 20 million doses on the way
Ghana and Nigeria have become the first two nations to approve Oxford’s vaccine against malaria.
Hollow “seed” shrinks cancerous tumors from the inside
A new drug delivery system for pancreatic tumors could dramatically decrease medication dosages, helping minimize unpleasant side effects.
The imagination effect: A history of placebo power
The famous placebo effect has a long, rich history — it certainly had an outsized role in the medicine of centuries past.
Alzheimer’s disease: an illness that needs a long overdue cocktail
Scientists are starting to agree that the "holy grail" solution for Alzheimer's is more likely to be a drug cocktail than a single treatment.
LSD effective as major depression therapy in phase 2 trial
MindMed and University Hospital Basel have announced top line results for their phase 2 trial.
Scientists train ants to sniff out cancer in just 30 minutes
Ants were just as accurate as cancer-sniffing dogs. Better yet, they could be trained in minutes rather than months.
Study finds CPR patients may frequently have near-death experiences
In a study of CPR patients across the US and UK, researchers found new evidence about near-death experiences.
Nurses are breaking the mold to set out on their own
Tech platform Hydreight wants to help nurses go into business for themselves by being a turnkey solution.
Some cancers shouldn’t be treated
We're detecting and aggressively treating more tumors than ever before. But we're also over-treating more cancers then ever.
“Nanosyringes” can inject medicine into a single cell
MIT researchers have turned a system found in bacteria into programmable “nanosyringes” for injecting proteins into human cells.
One shot could stop severe bleeding and save thousands of lives
A potentially lifesaving treatment to stop severe postpartum hemorrhage could soon be more accessible to the people who need it the most.
One way to speed up clinical trials: Skip right to the data with electronic medical records
It takes around 17 years for medical research to translate into clinical practice — why not use EMR data to speed things up?
New drug delivery tech could ensure you never forget your meds
Rice University's new drug delivery tech uses biodegradable microparticles to administer medications exactly when and where they are needed.
Tuberculosis kills over a million people a year. New breakthroughs may help humanity fight back.
The world needs a tuberculosis vaccine, but the challenge trials that could help are impossible to run. Two new approaches look to change that.
Epilepsy surgery has a success rate of only 50%. This digital brain may change that.
Using patient data and AI, French researchers have created a digital model of the brain to figure out which brain region needs removed.
Viruses cause 200+ diseases. This one drug may be able to treat them all.
New Zealand-based startup Kimer Med wants to create an antiviral that would be effective against many known viruses — and unknown.
New mRNA therapy could bring an end to peanut allergies
A new peanut allergy treatment based on mRNA could potentially lead to therapies that prevent all types of allergies in people.
Narcan is now available over-the-counter in the US
Naloxone administered by nasal spray can be a lifesaving drug with minimal side effects. It's now approved for over-the-counter use in the U.S.
How close are we to reversing paralysis?
Thanks to groundbreaking innovations in neuroscience, we’re seeing that forms of paralysis long assumed to be permanent can be reversed.
This man is trying to live underwater for a record-breaking 100 days
Biomedical engineer Joseph Dituri is attempting to break a world record by living in an underwater habitat for 100 days.
3D-printing the brain’s blood vessels with silicone could personalize neurosurgery
3D printing could make blood vessel replicas with the soft feel and the structural accuracy surgeons need.
Saliva: The next frontier in cancer detection
Scientists are finding tumor signals in spit that could be key to developing diagnostic tests for various types of cancer
Spread of deadly cancer delayed by organ transplant drug
A groundbreaking discovery on how pancreatic cancer spreads could lead to better therapies for the hard-to-treat disease.
Bird flu is everywhere. Are the vaccines ready?
As avian influenza continues to devastate the bird population and jump into mammals, scientists are preparing to protect two important groups.
Pfizer’s nasal spray for migraines is heading to pharmacies
The FDA has approved Pfizer’s zavegepant, a nasal spray for migraines that can ease pain in as few as 15 minutes.
Here’s how your sleep affects your immune system
Researchers found that patients who slept less than six hours a night were 27% more likely to have an infection.
Canadian students discover EpiPens will turn toxic in space
Canadian students launched EpiPen solution into suborbital space, and what came back was no longer life-saving medicine.
A single injection of stem cells slashes risk of heart attack or stroke by 58%
An injection of stem cells reduced the risk of heart attack or stroke by 58% in a trial of people with heart failure.
Does online opioid treatment work?
A sudden shift to virtual health care has increased access — and possibly outcomes — for patients with opioid use disorder.
Volunteers were purposefully infected with COVID-19. Was it worth it?
It has been a year since the first COVID human challenge data was published. What did we learn, and can HCTs prepare us for the future?
New drug could extend lives of people with deadly bone cancer
A new drug might extend the lives of people with bone cancer without subjecting them to painful or unpleasant treatments.
Scientists inject stem cells into the brain of Parkinson’s patient
A new stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease has just been administered to the brain of a person for the first time.
New transplant technique cures type 1 diabetes in monkeys
Massachusetts General researchers have developed a new form of transplantation that cured type 1 diabetes in monkeys.
Tirzepatide: A novel obesity drug ushers in a new era of weight loss — because this one works (Updated)
Patients who received tirzepatide in a recent clinical study lost more than 20% of their body weight (52 pounds, or 23.6 kg).
Oral bacteria trigger rheumatoid arthritis flare-ups
Periodontal (gum) disease is more common in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, implicating the former in causing the latter.
First at-home test can tell you if it’s COVID or flu
The FDA has granted authorization to an at-home test that can tell COVID from flu, the first of its kind.
New MS treatment targets the gut microbiome
We may be able to prevent chronic inflammation in multiple sclerosis patients by manipulating their gut microbiomes.
Small wonders: The antibodies from camels and sharks that could change medicine
A handful of animals make a pared-down version of our own antibodies. Scientists hope to harness them as treatments for human illnesses.
New light therapy could make cancer treatment better and safer
A new light-activated cancer treatment developed in the UK could make existing therapies better and safer.
A new look at the strange case of the first gene-edited babies
Did He Jiankui "Make People Better"? A new documentary leans toward a different narrative about gene-editing than we've heard before.
This $1 pill cuts binge drinking
Naltrexone, a medication that costs less than $1 per dose, helped people cut back on their binge drinking in a small study
A single dose of an old drug could save 2 million mothers from sepsis every year
A large international study has found that a single oral dose of a common antibiotic can “significantly” reduce the risk of maternal sepsis
How diet influences the conflict between cell “cooperators” and “cheaters”
Cancer-protective microbes support cooperative behaviour by bodily cells, but cancer-inducing microbes undermine it.
New CAR-T therapy shows promise against ovarian tumors
A CAR T-cell therapy that’s effective in mice with ovarian cancer may bring us closer to using the blood cancer treatment against tumors.
Scientists have discovered how to make almost any vaccine more potent
An approach called “rational vaccinology” could allow us to design more powerful vaccines, just by rearranging their ingredients.
“Brain-eating” amoeba beaten by old European drug
A man infected by a deadly brain-eating amoeba is on the road to recovery thanks to a decades-old drug used to treat urinary tract infections.
New evidence that teeth can fill their own cavities
Researchers find that, in some cases, tooth dentin can be regrown instead of needing to be replaced with man-made composite.
ChatGPT-like AI creates new bacteria-killing proteins
Using a large language model AI, biotech startup Profluent has created new antimicrobial proteins.
Simple tweak to cancer treatment reduces relapse risk by 28%
Delivering chemotherapy to colon cancer patients before and after surgery — instead of just after — reduces their risk of recurrence by 28%.
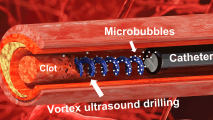
This “ultrasound vortex” can quickly clear blood clots
Using spiraling ultrasound waves, researchers hope to remove stroke-causing blood clots faster and safer.
Microbiome-safe method could head off Staph infection
A microbiome-friendly method of controlling Staph colonization has aced phase 2 clinical trials.