Field: Medicine
Has the US reached “peak obesity”?
A CDC survey suggests America’s obesity rate may be falling. Is this a turning point in the obesity epidemic? Or just a temporary plateau?
The exciting research that may cure Parkinson’s
GeneCode is developing a drug it hopes won't just alleviate Parkinson's symptoms but also protect and restore patient's neural health.
Ray Kurzweil explains how AI makes radical life extension possible
Life expectancy gains in developed countries have slowed in recent decades, but AI may be poised to transform medicine as we know it.
How Google’s new AI could revolutionize medicine
Google DeepMind's AlphaFold 3 could be the future of drug discovery — and the journey to its creation started more than a century ago.
Revolutionary weight-loss drugs like Wegovy come with a catch
People taking GLP-1 agonists are losing too much muscle, but these drugs designed to prevent muscle loss could solve the problem.
Are weight-loss meds the next wonder drugs?
Evidence is mounting that GLP-1 agonists could treat many health issues — including ones that aren’t obviously related to weight.
Milk could overcome one of the biggest hurdles to RNA therapies
RNA therapies typically break down if administered orally, but particles found in cows’ milk could provide perfect protection.
See how Moderna is using OpenAI tech across its workforce
A partnership between Moderna and OpenAI provides a real-world example of what can happen when a company leans into generative AI.
OpenAI’s GPT-4 outperforms doctors in another new study
OpenAI’s most powerful AI model, GPT-4, outperformed junior doctors in deciding how to treat patients with eye problems.
AI can help predict whether a patient will respond to specific tuberculosis treatments
Instead of a one-size-fits-all treatment approach, AI could help personalize treatments for each patient to provide the best outcomes.
In a future with brain-computer interfaces like Elon Musk’s Neuralink, we may need to rethink freedom of thought
In a future with more "mind reading," thanks to computer-brain interfaces, we may need to rethink freedom of thought.
Personalized cancer vaccines are having a moment
Personalized cancer vaccines were a recurring theme at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research in 2024.
When an antibiotic fails: MIT scientists are using AI to target “sleeper” bacteria
Most antibiotics target metabolically active bacteria, but AI can help efficiently screen compounds that are lethal to dormant microbes.
What’s next for COVID-19 drugs?
Paxlovid may have underperformed in a new trial, but other promising COVID-19 drugs are being authorized or in the works.
Old drug appears to halt progression of Parkinson’s motor symptoms
A GLP-1 agonist used to treat diabetes appeared to halt the progression of Parkinson’s symptoms in a phase 2 trial.
One-shot gene therapy reverses vision loss in small trial
A gene therapy for wet AMD — the most common cause of severe vision loss in seniors — is now in phase 3 trials.
How patients are using technology to kick-start a healthcare revolution
Susannah Fox, former chief technology officer for the HHS, explains how technology can empower a patient-led healthcare revolution.
Pacemaker powered by light eliminates need for batteries and lets the heart to function more naturally
Scientists designed a pacemaker that transforms light into bioelectricity, or heart cell-generated electrical signals.
Generative AI tech is dreaming up new antibodies
A new tool for designing antibodies relies on the same kind of tech underpinning DALL-E and other image-generating AIs.
Pill to prevent Lyme disease kills ticks before they can infect you
A pill to prevent Lyme disease quickly killed ticks that bit treated volunteers, suggesting it could slow the spread of tick-borne diseases.
Drugs made in space “cooked real good,” says startup
Varda Space Industries has shared the results of its first mission to manufacture "space drugs" in Earth's orbit.
Soaring insulin costs? Cows could help.
A genetically engineered cow that produce milk containing with human insulin could help cut the cost of the life-saving diabetes med.
FDA approves weight-loss drug Wegovy to treat heart problems
The FDA has approved the use of Novo Nordisk’s popular weight-loss drug Wegovy to reduce the risk of certain major heart issues.
Digital twins are an effective new way to control your metabolism
Digital twins: pioneered at NASA, innovated at Tesla, and now available for your own body, in a smartphone app.
Implantable solar cells could one day help restore vision
Australian researchers are developing tiny implantable solar cells that could be inserted into the eye to help restore vision.
Clinical trials can save more lives, and faster, with AI
The type of AI powering ChatGPT could help accelerate drug development by matching patients with clinical trials and vice versa.
Weight-loss drug reduces cravings for opioids in small study
A first-of-its-kind trial found that GLP-1 agonists, a popular kind of weight-loss drug, could help people overcome their opioid cravings.
The untapped potential of stem cells in menstrual blood
Stem cells found in menstrual blood could unlock new therapies and diagnostic tests, some researchers argue.
Evidence that gamma rhythm stimulation can treat neurological disorders is emerging
Researchers survey the therapeutic potential of noninvasive sensory, electrical, or magnetic stimulation of gamma brain rhythms.
New pharma supergroup aims to tackle skin disorders
Six biotech companies just merged to form Alys Pharmaceuticals with the goal of developing new treatments for skin disorders.
How to stop our immune systems from turning on us
From "inverse vaccines" to repurposed cancer therapies, several potential cures for autoimmune diseases are showing serious promise.
New hope for early pancreatic cancer intervention via AI-based risk prediction
To train their machine learning models, MIT researchers used electronic health record data from various institutions across the U.S.
One-shot CRISPR treatment for inherited disease aces first human trial
A CRISPR treatment for hereditary angioedema significantly reduced swelling attacks in its first human trial.
New non-opioid pain reliever moves closer to approval
Vertex Pharmaceuticals’ new painkiller, VX-548, significantly reduced moderate-to-severe pain in two phase 3 trials.
Inhalable sensors could enable early lung cancer detection
MIT engineers have designed diagnostic particles that can be aerosolized and inhaled to find cancer-associated proteins in the lungs.
Anti-aging pill for senior dogs is now in clinical trials
An anti-aging pill for senior dogs now in clinical trials might lead to treatments that extend human lives, too.
New antiviral shortens COVID-19 by 1.5 days
People taking simnotrelvir, a new antiviral treatment for COVID-19, felt almost immediate symptom relief and got better 1.5 days faster.
A dietician explains “Zepbound,” the newest weightloss drug
Zepbound recently joined the list of obesity-fighting drugs administered as injections that has been approved by the FDA.
One-and-done anti-aging treatment “rejuvenates” old mice
CAR-T cells that have been modified to target senescent cells could be a one-and-done anti-aging treatment.
Drinking this foam could boost an experimental cancer therapy
A drinkable foam packed with carbon monoxide molecules appears to boost the cancer-killing effects of autophagy inhibitors.
Deaf boy hears within days of receiving new gene therapy
A gene therapy designed to treat a rare form of genetic deafness has restored hearing in the first patient to receive it.
DeepMind’s AI could accelerate drug discovery
A new study suggests that AlphaFold, DeepMind’s AI tool for predicting protein structures, could be useful for drug discovery after all.
Pig liver filters blood outside a person’s body for 72 hours
A gene-edited pig liver that filtered the blood of a person who was brain dead for 72 hours could one day help people with liver failure.
Urine-propelled nanobots shrink bladder tumors by 90% in animals
Tiny, radioactive nanobots propelled by urine shrank bladder tumors by 90% in mice, suggesting a new way to target the disease.
Ultrasound waves help Alzheimer’s drug get into the brain
Beaming focused ultrasound waves into the heads of Alzheimer’s patients helped a drug bypass the blood-brain barrier.
Engineers develop a vibrating, ingestible capsule that might help treat obesity
MIT engineers designed an ingestible capsule that vibrates within the stomach, creating an illusory sense of fullness and reducing appetite.
Are anxiety and depression social problems or chemical disorders?
As antidepressants will soon be a $16B industry, the chemical imbalance theory suits business interests better than health interests.
Using AI, MIT researchers identify a new class of antibiotic candidates
Using a type of artificial intelligence, MIT researchers have discovered a class of compounds that can kill drug-resistant bacteria.
Psychoactive drug ibogaine helps veterans with TBI
A small study found that one dose of ibogaine could reduce the symptoms of a traumatic brain injury (TBI) for military vets.
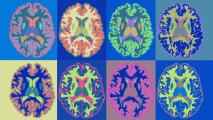
How a mutation in microglia elevates Alzheimer’s risk
A study finds that microglia with mutant TREM2 protein reduce brain circuit connections, promote inflammation, and contribute to Alzheimer’s.
Superbug-killing antibiotic is now in human trials
A promising new antibiotic that kills a superbug resistant to nearly all available drugs is now being tested in people.
Nutrition professor answers: Does chicken soup really help when you’re sick?
Is chicken soup just a comforting placebo, providing psychological benefit while we’re sick, without an actual therapeutic effect?
Moderna’s mRNA cancer vaccine works even better than thought
Adding Moderna’s mRNA cancer vaccine to a standard melanoma treatment dramatically reduces the risk of death or recurrence.
The 5 most exciting clinical trial results of 2023
In 2023, several potentially game-changing meds, including ones to treat pain and high cholesterol, showed huge promise in human trials.
Chemobrain is real. Here’s what to expect after cancer treatment.
Chemobrain, or chemofog, can significantly affect cancer survivors' quality of life with its social, psychological, and economic impacts.
Experimental implant could end the need for insulin injections
An arm implant containing islet cells could one day make it far easier for people with type 1 diabetes to manage their disease.
Researchers engineer insulin-releasing cells that respond to sound waves
New research in mice attempts to eventually replace insulin injections with the sounds waves of rock music.
This startup is solving the biggest problem to creating drugs that work
Lab-grown human tissues could revolutionize drug development. This AI-powered robot can create and test 10,000 of them at once.
Study: chronic pain’s root cause could be a process in the brain
Understanding that chronic back pain originates from within the brain could lead to quicker recovery, a new study finds.
Bad sleep worsens pain. Researchers may have discovered why.
Inadequate sleep worsens pain, which makes it difficult to sleep. This cycle may stem from disruptions to the body's endocannabinoid system.
Lidocaine makes cancer cells self-destruct, study finds
Lidocaine, a common local anesthetic, activates proteins that cause certain types of cancer cells to self-destruct.
Stem cell injections could be the key to curing MS
From promising stem cell therapies to EBV vaccines, researchers are closer than ever to finding a cure for MS.
Cholesterol drug suggests new way to treat Alzheimer’s
A cholesterol drug that reduced brain damage in mice could reveal a new approach to treating Alzheimer’s disease in people.
First anti-aging drug for dogs nears approval
The FDA is a major step closer to approving biotech company Loyal's LOY-001, the first anti-aging drug for dogs.
Australia’s 30-year quest to unlock an ancient painkiller
A crocodile attack led to a 30-year partnership to develop a painkiller based on the Nyikina Mangala people's traditional knowledge.
Experimental drug cuts heart disease risk factor by 96%
Eli Lilly’s experimental drug lepodisiran reduced blood levels of lipoprotein(a) by up to 96% in a small trial.
Human brains have a remarkable ability to rewire themselves following injury
Every brain injury is unique, as is every person’s path to recovery. A concussion specialist explains the science behind rehabilitation and recovery.
World’s first CRISPR therapy approved in UK
UK regulators have authorized CRISPR Therapeutics’ Casgevy, making it the world’s first approved CRISPR therapy.
Wegovy slashes heart attack risk by 28%
Novo Nordisk’s weight-loss drug Wegovy can reduce a person’s risk of a serious cardiovascular event by 20%.
New gene therapy reverses hearing loss in 4 children
A new gene therapy being trialed in China was able to reverse hearing loss in 4 of the 5 children to receive it.
New “super melanin” protects and heals skin
A “super-charged” synthetic melanin is even better at protecting the skin and healing damage than the natural kind.
Gold-laced gel could help you recover from a major muscle injury
A combination of electrical stimulation and a gold nanoparticle-laced hydrogel could one day help people recover from major muscle injuries.
Blocking this one protein could strengthen muscles
Stanford researchers have figured out how a therapy that blocks a single protein can reverse age-related muscle loss in mice.
CRISPR cure for HIV now tested in 3 people
Excision BioTherapeutics has shared data from the first human clinical trial of a CRISPR cure for HIV. Here's what we know — and don't know.
“Living pharmacies” could mean you never forget to take your meds again
The US government is funding the development of "living pharmacies," implants containing cells that release medications on demand.
“Hydrogel” drugs could suppress HIV with minimal treatments
An injectable solution that self-assembles into a hydrogel to deliver 6 weeks of anti-ARV drugs could make managing HIV less of a burden.
What the science really says about vitamin D deficiency
When is low vitamin D a potential concern? And when might you need to get your levels tested? Here's what the evidence says.
New “Lattice” device tests drugs on eight organs at once
Northwestern University scientists have developed a device that simulates up to eight organs at once to aid drug development.
Is iron the Achilles’ heel for cancer?
Some cancer cells store high quantities of iron. Iron-activated cancer drugs selectively disrupt cancer cells, without harming healthy cells.
Octopus tentacle-like patch delivers drugs through your cheek
A needle-free drug delivery system inspired by octopus tentacles could one day replace injections for administering biopharmaceuticals.
New “multipronged” gene therapy reverses paralysis in mice
A new gene therapy that guides nerve regeneration across complete spinal cord injuries restored the ability to walk in paralyzed mice.
An implantable device could enable injection-free control of diabetes
MIT engineers designed an implantable device that carries islet cells along with its own on-board oxygen factory to keep the cells healthy.
New “inverse vaccines” could be key to curing autoimmune disorders
"Inverse vaccines" that teach the immune system to tolerate triggering molecules could be the key to curing autoimmune disorders.
Tooth decay: Mouthwash turns your teeth blue when it’s time to go to the dentist
A mouthwash solution containing ferumoxytol and a dye could treat, prevent, and diagnose tooth decay, according to UPenn researchers.
Brain implant lets cancer patients try 20 different drugs at a time
A microdevice that injects up to 20 drugs into gliomas at once could help doctors quickly identify the best treatment for cancer patients.
A magnetic therapy for depression gains precision
Approved over a decade ago, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) could be effective if the treatment was tailored to individual brains.
Drug for MS may be able to treat Alzheimer’s, too
A drug approved to treat multiple sclerosis reduced neuroinflammation and improved memory in mouse models of Alzheimer’s.
Popular weight-loss drugs show promise as addiction treatments
New trials will test the ability of GLP-1 agonists, a popular class of weight-loss drugs, to help people beat addictions to drugs and alcohol.
Australian ant honey inhibits tough pathogens, new research shows
Honeypot ant honey may help develop our arsenal of effective antibacterial and antifungal treatments, which are increasingly vital.
At least 5 people have been cured of HIV. Is the AIDS pandemic ending?
A handful of people have already been functionally cured of HIV — and new, universal cures are just on the horizon.
New treatment slashes obesity in mice eating fatty, sugary diet
A new obesity treatment developed at UMass triggered weight loss in mice even as they continued to eat a diet high in fat and sugar.
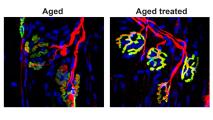
Transplants of lab-grown brain cells reduce Parkinson’s symptoms
Transplants of lab-grown dopamine neurons reduced the amount of time people experienced Parkinson’s symptoms in a small trial.
Artificial kidney aces test in pigs
An artificial kidney prototype just aced a pig trial, bringing it closer to human trials — and a step closer to ending the need for dialysis.
Potential heart attack treatment discovered in human placentas
Placental cells known to home in on and repair damaged heart cells in mice have been discovered in humans, too.
To stave off Alzheimer’s, protect your brain’s mitochondria
Mitochondria are crucial for memory preservation and are emerging as key players in the fight against Alzheimer's.
World-first experiment shows genetically engineered bacteria detecting cancer
Genetically engineered bacteria could be used to detect a range of different diseases, particularly infections and cancers.
Weight-loss drug improves heart failure symptoms, too
Novo Nordisk’s popular weight-loss drug semaglutide (Wegovy) improved heart failure symptoms in a trial of more than 500 people.
New obesity treatments could reshape the world
New obesity treatments, including GLP-1 agonists and gene therapies, could make it easier for people to lose weight and keep it off.
One-shot gene therapy for liver disorder works in a small trial
A new gene therapy for the rare liver disorder Crigler-Najjar syndrome was highly effective in a small trial.
Extreme treatment for alcoholism slashes drinking by 90% in monkeys
An in-development treatment for alcoholism dramatically reduced consumption in monkeys that previously drank heavily.