Field: Biology
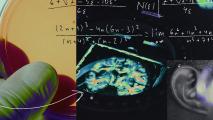
Arc Institute’s new AI can read and write the code of life
Training on the DNA of nearly 130,000 species taught Evo 2 how to generate DNA sequences the same way other AIs do text or images.
We’re able to create new creatures through gene editing. What’s stopping us?
The question isn’t whether we can sculpt new life. The question is what comes next.
How cryopreservation could end death as we know it
The technology could one day allow people with terminal illnesses to go into "hibernation" until a cure is found.
Revolutionary weight-loss drugs like Wegovy come with a catch
People taking GLP-1 agonists are losing too much muscle, but these drugs designed to prevent muscle loss could solve the problem.
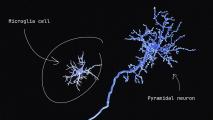
What hybrid mouse/rat brains are showing us about the mind
Modified mice with hybrid brains that include rat neurons could one day lead to new breakthroughs in neuroscience.
AI can help predict whether a patient will respond to specific tuberculosis treatments
Instead of a one-size-fits-all treatment approach, AI could help personalize treatments for each patient to provide the best outcomes.
When an antibiotic fails: MIT scientists are using AI to target “sleeper” bacteria
Most antibiotics target metabolically active bacteria, but AI can help efficiently screen compounds that are lethal to dormant microbes.
Scientists are deep-freezing corals to repopulate the ocean
Healthy corals could disappear by the 2030s if climate change is not curbed, so scientists are deep freezing specimens.
A protein found in human sweat may protect against Lyme disease
Human sweat contains a protein that may protect against Lyme disease, according to a study from MIT and the University of Helsinki.
Pacemaker powered by light eliminates need for batteries and lets the heart to function more naturally
Scientists designed a pacemaker that transforms light into bioelectricity, or heart cell-generated electrical signals.
How our “junk DNA” led to humans being tailless
A CRISPR study out of NYU suggests that junk DNA likely led humans to evolve to be tailless millions of years ago.
OpenBCI’s new VR headset reacts to your brain and body
OpenBCI is reshaping the relationship between humans and the virtual world with Galea Beta, a headset that measures the body and brain.
The untapped potential of stem cells in menstrual blood
Stem cells found in menstrual blood could unlock new therapies and diagnostic tests, some researchers argue.
Bioluminescent plants don’t exist in nature — but you can buy one for $29
Biotech firm Light Bio is selling gene-edited bioluminescent plants that glow green in the dark for just $29.
Netflix’s “You Are What You Eat” proves twin studies’ importance to science
What is it that makes twins so special, and how do researchers harness the power of twins? "You Are What You Eat" helps prove their importance.
Inhalable sensors could enable early lung cancer detection
MIT engineers have designed diagnostic particles that can be aerosolized and inhaled to find cancer-associated proteins in the lungs.
“Insane” new type of virus-like organisms found in human gut
Stanford scientists have discovered a strange new class of virus-like organisms, called “obelisks,” in the human gut microbiome.
The growing link between microbes, mood, and mental health
New research suggests that to maintain a healthy brain, we should tend our gut microbiome not through pills and supplements, but better food.
No pain, no gain? Science debunks yet another exercise myth
Exercise culture advertises intense workouts as the best way to see gains. But research suggests moderate exercise is better.
DeepMind’s AI could accelerate drug discovery
A new study suggests that AlphaFold, DeepMind’s AI tool for predicting protein structures, could be useful for drug discovery after all.
Using AI, MIT researchers identify a new class of antibiotic candidates
Using a type of artificial intelligence, MIT researchers have discovered a class of compounds that can kill drug-resistant bacteria.
Bioengineers design a new plant to purify air faster than nature
Neoplants has bioengineered a pothos plant that removes 30 times more pollutants from the air than a regular houseplant.
The most damaging exercise myth
It's a common belief that it's normal for adults to be less physically active as they age. This might be the most pernicious exercise myth.
Cyborg computer combining AI and human brain cells really works
A new biohybrid computer combining a “brain organoid” and a traditional AI was able to perform speech recognition.
Mice could someday become venomous, suggests study on the evolution of oral venom systems
Although scientists have a good understanding of the composition of snake venom, little is understood about the origins of venom systems.
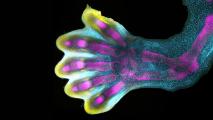
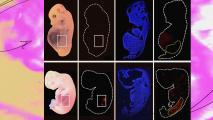
Stunning video reveals how our fingers form in the womb
A first-of-its-kind map of human limb development could help prevent a common type of birth defect in the future.
Untangling the genetics that underlie our facial features
Hundreds, if not thousands, of genes affect the shape of the face, in subtle ways. Researchers explain why, and how, we look like our family.
Why do women live longer than men?
Women tend to live longer than men around the world – but the gap life expectancy is not a constant. These stats tell the story.
Researchers engineer insulin-releasing cells that respond to sound waves
New research in mice attempts to eventually replace insulin injections with the sounds waves of rock music.
Tiny biobots surprise their creators by healing wound
Tiny “biobots” made from human windpipe cells, amazingly, helped damaged neural tissue to repair itself in a new study.
This startup is solving the biggest problem to creating drugs that work
Lab-grown human tissues could revolutionize drug development. This AI-powered robot can create and test 10,000 of them at once.
Bad sleep worsens pain. Researchers may have discovered why.
Inadequate sleep worsens pain, which makes it difficult to sleep. This cycle may stem from disruptions to the body's endocannabinoid system.
Search algorithm reveals nearly 200 new kinds of CRISPR systems
Researchers have discovered rare new CRISPR systems that have a range of functions and could enable gene editing, diagnostics, and more.
Exposing plants to an unusual chemical early on may bolster their growth and help feed the world
"Priming" plants by exposing them to certain chemicals while they’re seeds can affect their growth later in life.
Human sleep patterns appear to change with the seasons
Researchers observed the sleep of 188 subjects to see if their slumbers would change in duration and structure along with the seasons.
“Iron Man” material made from DNA and glass is 4x stronger than steel
Using only DNA and glass, researchers made a material four times stronger and five times lighter than steel. It was inspired by Iron Man.
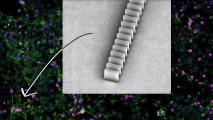
Ex-NASA engineer Mark Rober created the world’s smallest Nerf gun — from DNA
Mark Rober and Pallav Kosuri created a Nerf gun so tiny they had to build it out of DNA. This DNA "origami" has the potential to revolutionize engineering.
Sex life discovery raises IVF hope for endangered purple cauliflower soft coral
The purple cauliflower soft coral Dendronephthya australis, now listed as an endangered species, has a new hope of survival with IVF.
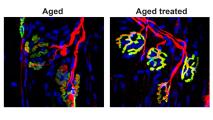
Blocking this one protein could strengthen muscles
Stanford researchers have figured out how a therapy that blocks a single protein can reverse age-related muscle loss in mice.
“Living pharmacies” could mean you never forget to take your meds again
The US government is funding the development of "living pharmacies," implants containing cells that release medications on demand.
Rancid food smells and tastes gross − AI tools may help scientists prevent that spoilage
A group of chemists are using artificial intelligence to extend the life of food products, by teaching AI models about rancidity.
What BMI can’t tell us about our health
Body mass index (BMI) continues to be the go-to tool for medical doctors and population researchers despite saying little about our health.
New weight loss drug acts like an “exercise pill”
A new candidate weight loss drug called SLU-PP-332 was found to boost muscular and aerobic endurance in mice.
“The twin boom”: why twinning is on the rise
Since the 1970s, the rate that twins are born has doubled in most developed countries. What caused this and is it going to change soon?
Exercise scientist explains what your daily step goal should be by your weight
Tracking daily step counts can be a useful tool for weight management, but only if you tailor it to your own body weight.
What the science really says about vitamin D deficiency
When is low vitamin D a potential concern? And when might you need to get your levels tested? Here's what the evidence says.
Why this startup is creating edible oil from sawdust
ÄIO's main goal is to replace palm oil with oil upcycled from low-value industry organics in order to prevent further deforestation.
Stanford plans to put a 3D-printed human heart in a pig by 2028
Using 3D bioprinting, scientists are trying to construct perfect replacements for damaged organs, bones, and tissues.
Ever wonder how your body turns food into fuel? We tracked atoms to find out
New research offers new way to understand our metabolism in unprecedented detail, identifying four distinct phases of the process.
What does the evidence say about omega-3 fats for heart disease, dementia, and arthritis?
Are fish oil supplements as good for preventing heart disease, dementia, and other health conditions as we think? Or is eating fish better?
Jellyfish surprise scientists by learning without a brain
Researchers demonstrate that Caribbean box jellyfish don't just float around aimlessly. They learn and adapt to their environment.
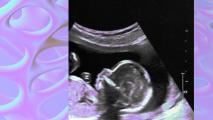
Artificial wombs for preemies move closer to human trials
A panel of FDA advisors has met to discuss the development of artificial wombs designed to help extremely premature babies survive.
An implantable device could enable injection-free control of diabetes
MIT engineers designed an implantable device that carries islet cells along with its own on-board oxygen factory to keep the cells healthy.
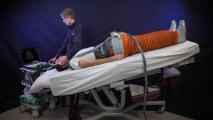
Spending time in space can harm the human body − but scientists are working to mitigate these risks before we go to Mars
With NASA planning more missions to space in the future, scientists are studying how to mitigate health hazards that come with space flight.
Can you speed up your metabolism? And should you?
Our metabolism is the force inside our bodies that mysteriously decides whether to convert food into energy or weight.
Molecule reduces inflammation in Alzheimer’s models
A potential new Alzheimer’s drug represses the harmful inflammatory response of the brain’s immune cells, improving cognition in tests.
Scientists grow “human-ish” organs in pigs for the first time
Partially human kidneys have been grown in pig embryos, marking the first example of anyone growing solid human organs in another species.
Can’t afford a gym membership? Add these 3 things to your workout routine
With gym memberships and fitness classes are becoming increasingly unaffordable, you can make just as much progress at home.
Australian ant honey inhibits tough pathogens, new research shows
Honeypot ant honey may help develop our arsenal of effective antibacterial and antifungal treatments, which are increasingly vital.
World-first experiment shows genetically engineered bacteria detecting cancer
Genetically engineered bacteria could be used to detect a range of different diseases, particularly infections and cancers.
Scientists bioengineer plants to have an animal-like immune system
Scientists have bioengineered a hybrid molecule by fusing components from an animal's and a plant's adaptive immune system.
Breakthrough creates stem cells without any “memories”
A new method for creating induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells includes a memory reset that puts the cells in a more embryonic-like state.
“Light sculpting” chip can rapidly test for thousands of diseases
Stanford researchers have developed a new type of molecular test that works without a cumbersome amplification step.
Scientists discover a gel that whitens teeth and kills 94% of bacteria
Scientists have found that light-activated oxidizing nanoparticles can whiten teeth without causing damage.
Too much body fat isn’t the problem — malfunctioning body fat is
When fat cells are overloaded with excess nutrients, they become too big and don't receive enough oxygen, causing them to die.
Scientists make pain relievers like Tylenol from pine trees rather than fossil fuels
Chemists have shown how to manufacture ibuprofen and acetaminophen using a waste product from the forestry and paper industries.
Nematodes survive 46,000 years on ice
A pair of nematodes from the Pleistocene survived in the Siberian permafrost by entering a survival state known as cryptobiosis.
Fragile X syndrome often results from improperly processed genetic material
Researchers discovered that the mutated gene responsible for fragile X syndrome is active in most people with the disorder, not silenced.
Northern white rhinos are set for extinction. Only a technological moonshot can save them.
Project BioRescue aims to create the reproductive technology necessary to resurrect the northern white rhino. But time is running out.
Lab-grown meat techniques aren’t new
Cell cultures are common tools in science, but bringing them up to scale to meet society’s demand for meat will require further development.
Immune cells in the brain may reduce damage during seizures and promote recovery
Microglia perform many functions in the brain, and their role in seizures is unclear — a new study in mice aims to find out more.
Why death matters
Reframing life in terms of death reveals some of the biggest philosophical problems with how we think about living systems.
Startup aims to transplant pig hearts into kids in 2024
eGenesis hopes to transplant pig hearts from genetically engineered swine into young children with serious heart defects by 2024.
Fiber is your body’s natural guide to weight management
Fiber is important not just for happy bowel movements, but also for your blood sugar, weight, and overall health.
Exercise may or may not help you lose weight and keep it off
There isn’t a debate on the overall health benefits of regular exercise, but scientists don't agree on whether it actually keeps weight off.
Aging is complicated – a biologist explains why no two people or cells age the same way
While some people may be older in chronological age, their biological age might be much younger. A biologist explains why.
Not all repellents are equal – here’s how to avoid mosquito bites this summer
Researchers studied different types of mosquito repellents and their efficacy for over a decade. Here's what they found.
Quantum biology: Your nose and house plants are experts at particle physics
Quantum processes, normally associated with the very small or very cold, have been found to occur in biological systems. This was unexpected.
“Zombie” cells are the key to a tiny sea creature’s full-body regeneration
A tiny sea creature’s regenerative abilities add to the growing evidence that senescent cells aren’t always detrimental.
Can we train our taste buds for health?
Reformulating foods tailored to the plasticity of our taste buds could be a practical and powerful tool to promote health.
Cryogenically frozen organs successfully transplanted into rats for the first time
Thanks to a new "nanowarming" technique, scientists have successfully transplanted cryogenically frozen organs into rats for the first time.
“Backdoor” into the ear offers new hope for reversing deafness
A new study has unlocked a “backdoor” into the inner ear that could make administering gene therapies to restore hearing less risky.
There’s now a wearable that can track your stress hormones
A wearable device called U-RHYTHM makes it easy for researchers to see how stress hormones ebb and flow over 24 hours.
Plants perform quantum mechanics feats that scientists can only do at ultra-cold temperatures
There may be a link between quantum mechanics and photosynthesis explaining why plants are so effective at converting light to food.
“Spooky” quantum biology might cause your DNA to mutate
Research suggests that quantum effects could drive mutations in human DNA — the latest development in the emerging field of quantum biology.
How intestinal viruses could help you live to be 100
People who live past age 100 have a greater diversity of bacteriophages (that is, viruses that infect bacteria) in their intestines.
Model human embryo, created from stem cells, survives past two weeks
A model human embryo capable of developing past day 14 could revolutionize our understanding of human development.
Have we got the brain all wrong? Study shows its shape is more important than its wiring
Neural activity may be more influenced by the shape of the brain – its grooves, contours, and folds – than by its complex interconnections.
Visiting space likely won’t cause permanent brain damage, says NASA study
Spending months in space has a major impact on astronauts’ brains, but three years back on Earth appears to reverse the change.
Scientists are growing animals in artificial wombs. Humans might be next.
Artificial wombs promise to give people a way to have biological children without putting their own health at risk.
The neurons that make us feel hangry
Researchers gave pinpointed a cluster of cells called AgRP neurons near the underside of the brain that may create “hangry” feelings.
Sound waves can trigger torpor-like state in mice and rats
Ultrasound stimulation triggers a torpor-like state in animals, suggesting a noninvasive way to put people into the state.
Gain-of-function research is more than just tweaking risky viruses
Gain-of-function experiments in the lab can help researchers get ahead of viruses naturally gaining the ability to infect people in the wild.
Chronic pain can be objectively measured using brain signals
Even though pain is universal and we know it happens in the brain, we've never before had a way to objectively measure its intensity.
Here’s how growing plants on the Moon could benefit Earth
Making plants grow on the Moon could be instrumental in helping gardens to grow greener on Earth in the face of climate change.
Did life evolve more than once? Researchers are closing in on an answer
Current scientific consensus is that life emerged from non-living molecules in a process called abiogenesis. But if life emerged once, why not more times?
Older people were 3x stronger at the end of this science-backed 8-week program
But what if you’re in your 60s, 70s, 80s or 90s? Is it “too late” to build muscle and fight sarcopenia? Here’s what the research says.
We’re analysing DNA from ancient and modern humans to create a “family tree of everyone”
Genetic genealogy not only helps us understand where we came from, but it could also be used for tracing the origin of genetic mutations.
Like hungry locusts, humans can easily be tricked into overeating
Our bodies crave more food if we haven’t had enough protein — especially if we’re reaching for ultraprocessed foods.
Discovery finally uncovers how melanin blocks UV
An international team of researchers have isolated and analyzed a component of melanin, which protects us from the sun.